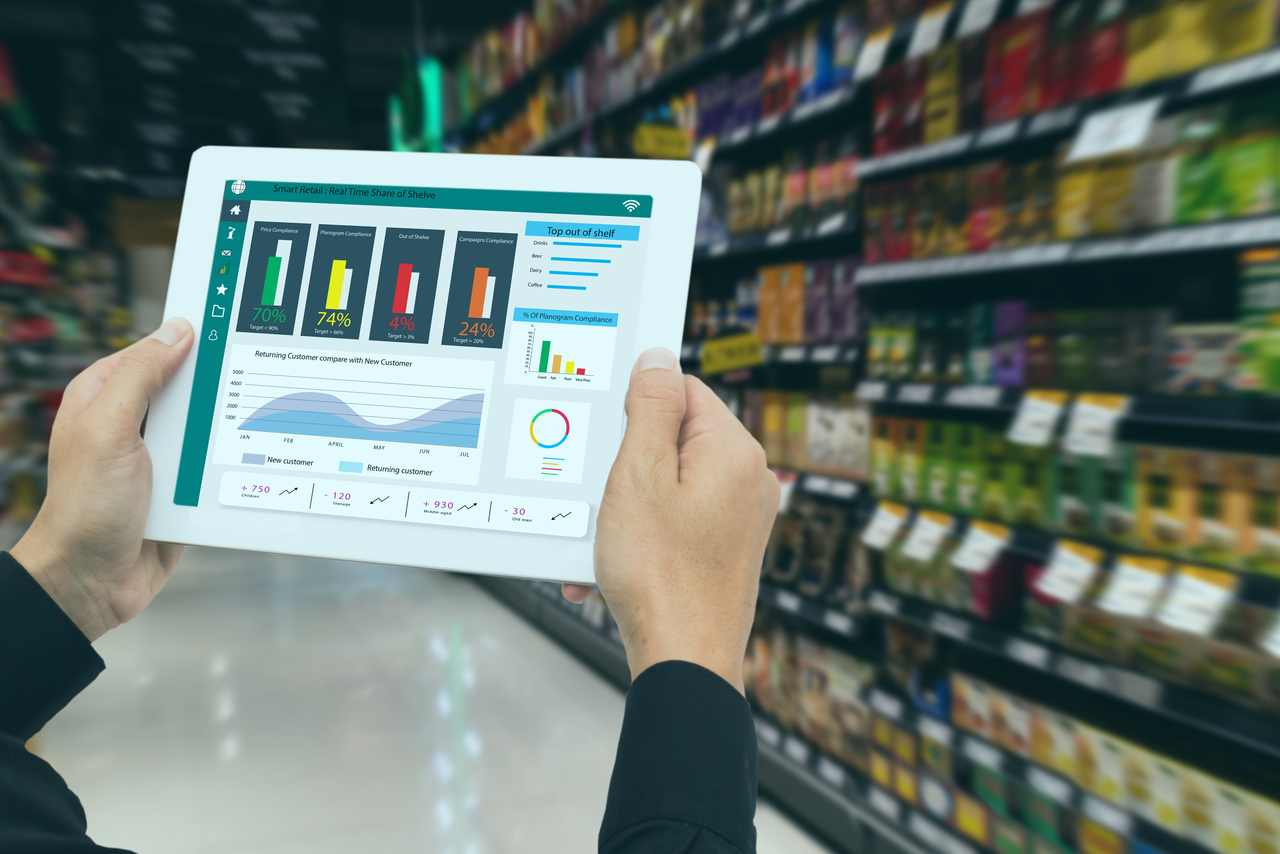
![]() The application of IoT to create intelligent, connected, interactive and personalized spaces help to achieve what is known as “Smart Spaces”. Smart Spaces can span across a building, an enterprise, location or even a city. Smart Spaces are customizable, energy efficient and intelligent and provide key insights into usage allowing better planning and optimisation.
The application of IoT to create intelligent, connected, interactive and personalized spaces help to achieve what is known as “Smart Spaces”. Smart Spaces can span across a building, an enterprise, location or even a city. Smart Spaces are customizable, energy efficient and intelligent and provide key insights into usage allowing better planning and optimisation.
Intelligent Edge is an indispensable component to realise Smart Spaces. The intelligent edge refers to compute capability available in gateways and IoT devices that allow processing data as close as possible to its origin. This prevents sending the data to the backend which is normally a cloud or datacenter-based environment. There are various reasons why we need an intelligent edge component in smart spaces. These are:
- Critical event processing and alerts: Without an intelligent edge, a “Smart Spaces” solution would rely on components running on cloud or a data center to process the events and generate alerts. However, for critical events (e.g. fire, floods) which need real time action, sending the event details to the cloud first and then getting a response would be too slow (given the fact that during natural calamities, internet connections may become jittery). Hence, in this scenario, we need an intelligent edge component (e.g. intelligent gateway or even intelligent sensors) which can communicate with each other, create plan based on the prevalent conditions and then generate alerts. An example could be communication between fire sensors, automatic fire extinguishers, wind direction sensors etc. to understand the direction of spread of fire, alerting the region in line of fire first and determining which fire extinguishers to be used first.
- Better user experience: It is a known fact that if response from a user’s query (e.g. gesture, input) takes more than a couple of seconds, the users perceive it as a slow system and quickly lose interest. The same applies to smart spaces as well. If the user requests for navigational directions to specific conference room in an enterprise setup and the response takes a long time, the user will try to get this information from a person standing nearby rather than waiting for the system to provide the response. In this case, the role of intelligent edge becomes important, which should be able to generate the response quickly and provide a visual clue as well on how to reach the destination. The detailed response can then be provided on the user’s device via a QR code which redirects the user to specific site having response to his/her query.
- Better reliability: In many scenarios, smart space-based solutions send real time meter readings, consumption data or occupancy data to backend servers. However, in case of network issues, slow networks or disconnected internet, the data during the network downtime may be lost. To achieve better reliability in these scenarios, it is important that the edge component stores the meter readings, consumption or occupancy data locally and then send them to the backend when the connection is restored. This is possible when there is an intelligent edge that is able to buffer the data and send them to the backend.
- Reduction in network bandwidth requirements: An intelligent edge can process the data locally (e.g. sensor data, event data, logs etc.), generate the insights and send only the required information to the solution backend. This saves network bandwidth and also the amount of data that is to be stored on the databases. The ability of intelligent edge to filter out unwanted data allowing to save cost on bandwidth requirements and storage space requirements of the solution.
- Improved security: Sensitive data can be processed locally without being sent to the cloud. This reduces the risks of data leakage, reduces the attack surface and ensures compliance because some countries prevent sending data outside their geographical regions
Challenges with Intelligent Edge:
- Increase in cost: While intelligent edge does provide additional computer capacity, it leads to an increase in overall cost of the solution. To deal with this, it is recommended to have an intelligent edge gateway that caters to the need of multiple sensors and IoT devices (rather than having the edge intelligence in the sensors and IoT devices), allow to reduce the overall cost.
- Interoperability issues: The intelligent edge solutions provided by multiple vendors have their own stack and environments. In this case, it becomes difficult for solutions to work across vendors. There are some protocols like MQTT, LwM2M, CoAP which allow for these solutions to work with each other, but a complete replace of one edge solution by another is not always straightforward.
- Edge security: While intelligent edge offloads a lot of workloads from the cloud-based backend, but because, it is storing critical data, it requires additional security given the fact that the edge is not always in a protected environment and may have physical access. There are chances of theft and reverse engineering which may expose critical data. Hence, edge security is one of the major concerns to be addressed by the edge solution vendors.
With the advent of AI and faster communication technologies like 5G, Edge computing has become more powerful. It is indeed a technology that would grow and would play a critical role in shaping the world of Smart Space based solutions.