Introduction
The technology landscape is evolving rapidly, with generative AI (GenAI) emerging as a prominent force. However, as with any new technology, there is a significant amount of hype and uncertainty surrounding its potential. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the key trends shaping the AI landscape and provide actionable insights for tech providers.
The Gartner Hype Cycle for Generative AI
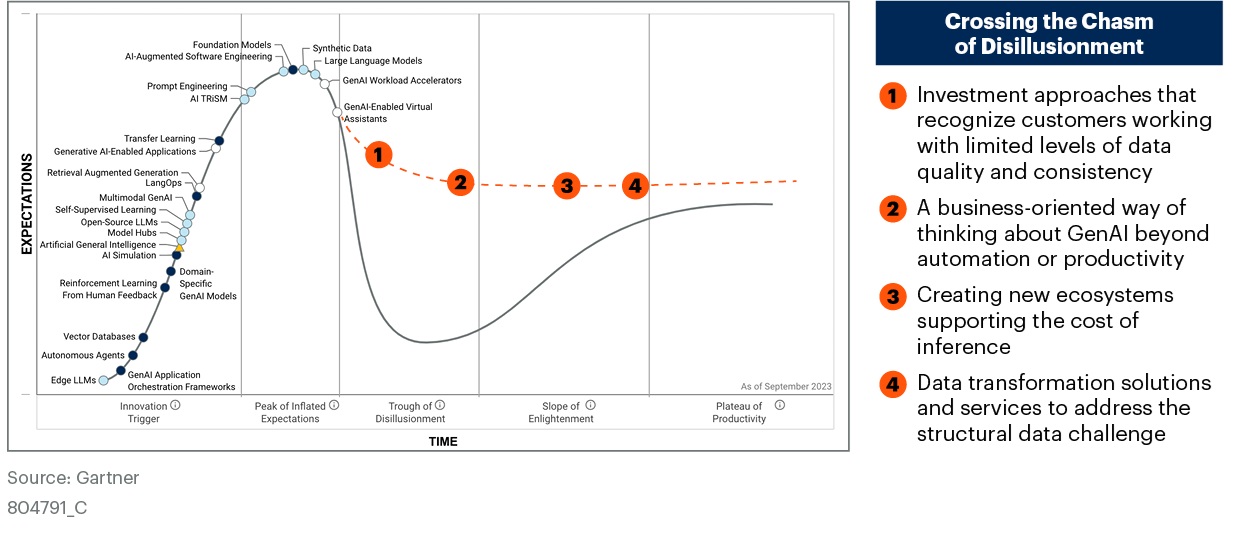
The Gartner Hype Cycle for Generative AI highlights the current state and future trends of generative AI technologies. The cycle is divided into five phases: Innovation, Inflated Expectations, Disillusionment, Enlightenment, and Productivity.
Key trends and technologies mentioned in the cycle include:
- Foundation Models and Large Language Models are the building blocks of many generative AI applications.
- Prompt Engineering is the process of crafting effective prompts to guide generative AI models.
- GenAI Workload Accelerators are hardware and software solutions that optimize the performance of generative AI models.
- AI TRiSM (Trust, Risk, and Security Management) is crucial for responsible and ethical deployment of generative AI.
- GenAI-Enabled Virtual Assistants can provide personalized assistance and support.
- Transfer Learning allows generative AI models to learn new tasks quickly.
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) combines retrieval of relevant information with generative AI to produce more accurate and informative outputs.
- LangChain is a framework for building applications with large language models.
- Multimodal GenAI can process and generate multiple types of data, such as text, images, and audio.
- Self-Supervised Learning enables generative AI models to learn from unlabeled data.
- Open Source LLMs are freely available models that can be customized for specific use cases.
- Model Hubs provide a platform for sharing and discovering pre-trained generative AI models.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a hypothetical type of AI that can perform any intellectual task that a human can.
- Domain-Specific GenAI Models are specialized for particular domains, such as healthcare or finance.
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback is a method for training generative AI models to align with human preferences.
- Vector Databases are used to store and retrieve large amounts of data efficiently.
- Autonomous Agents are AI systems that can act independently in the real world.
- Edge LLMs are generative AI models that run on edge devices, such as smartphones and IoT devices.
- GenAI Application Orchestration Frameworks help manage and coordinate multiple generative AI applications.
- Data Transformation Solutions and Services address the challenges of working with low-quality and inconsistent data.
In summary, the Gartner Hype Cycle for Generative AI suggests that these technologies are still in the early stages of adoption, but they have the potential to revolutionize many industries.
The Challenges and Opportunities of GenAI
While GenAI offers immense potential, it also presents significant challenges for tech providers. Some of the key challenges include:
- High Cost of Inference: The computational resources required to run GenAI models can be expensive, making it difficult for some organizations to justify the investment.
- Specialized Skills: Developing and deploying GenAI solutions requires specialized skills that may be in short supply.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI raises ethical concerns related to bias, privacy, and transparency.
- Data Quality and Quantity: GenAI models require large amounts of high-quality data to train effectively.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating GenAI solutions with existing IT infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities offered by GenAI are substantial. By leveraging GenAI, organizations can:
- Improve Efficiency: Automate tasks and processes, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value work.
- Enhance Customer Experience: Create personalized experiences and improve customer satisfaction.
- Drive Innovation: Start building innovative products and services that seemed impossible earlier.
- Gain a Competitive Advantage: Differentiate from competitors by leveraging AI to solve complex problems.
Key Recommendations for Tech Providers
Based on analysis of the current trends and challenges, the following recommendations can be made for tech providers:
- Move Beyond Add-ons: Create entire products based on business outcomes, changes, and new productivity measures.
- Extend Revenue and Margins: Develop products that offer more than basic use cases.
- Educate Customers: Help customers understand GenAI investments through tailored paths.
- Participate in GenAI Infrastructure: Forge alliances with application and infrastructure providers for efficiency and revenue.
- Embrace the Builder Culture: Foster a culture that encourages employees to innovate and create solutions. Provide them with the necessary tools, training, and support.
- Adopt a Strategic Approach to GenAI: Develop a clear roadmap for GenAI adoption that aligns with your organization’s goals and priorities. Consider factors such as the potential benefits, risks, and costs associated with GenAI.
- Prioritize Ethical AI: Ensure that your AI solutions are developed and deployed in an ethical manner. Consider factors such as bias, privacy, and transparency.
- Invest in Talent Development: Build a team with the skills and expertise needed to develop and deploy GenAI solutions. This may involve hiring new talent or upskilling existing employees.
- Collaborate with Partners: Partner with other tech providers, universities, or research institutions to access specialized knowledge and resources.
- Address Data Challenges: Invest in data quality and governance initiatives to ensure that your data is suitable for AI applications.
- Integrate GenAI with Existing Systems: Develop a plan for integrating GenAI solutions with your existing IT infrastructure.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the performance of your GenAI solutions and make necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
The future of technology is being shaped by the convergence of emerging trends like the Rise of the Builders and the transformative power of generative AI. By understanding these trends and adopting a strategic approach, tech providers can position themselves for success in the rapidly evolving AI landscape. It’s time to embrace the opportunities and navigate the challenges to build a future where AI empowers individuals and organizations to achieve their goals.
Glossary:
Significant (adjective) – noteworthy; sufficiently important/great or attention worthy:
Sequel (noun) – a published, broadcast, or recorded work that continues the story or develops the theme of an earlier one.