Blockchain, the decentralized and transparent ledger system has expanded its horizons to revolutionize various industries, with asset management being a prominent beneficiary. According to research conducted by grand view research, the market for asset management worldwide was estimated to be worth $58.02 billion in 2023 and is extrapolated to grow at a CAGR of 36.4% from 2024 to 2030.
Asset management refers to the process of planning and controlling the acquisition, operation, maintenance, renewal, and disposal of assets. This mechanism reduces associated costs and risks while maximizing the delivery potential of assets. Asset class includes manufacturing plants, infrastructure, buildings, and equipment under physical assets in addition to intangible assets like software licenses and intellectual property.
Challenges in Traditional Asset Management
High fees, potential conflict of interest among managers, and lack of transparency have all hindered traditional asset management. Effective decision making may be hampered by these problems which are exacerbated by outdated technology and delayed adoption of data analytics. Moreover, conventional asset management techniques continue to face difficulties from market volatility and regulatory changes.
Understanding Blockchain in Asset Management
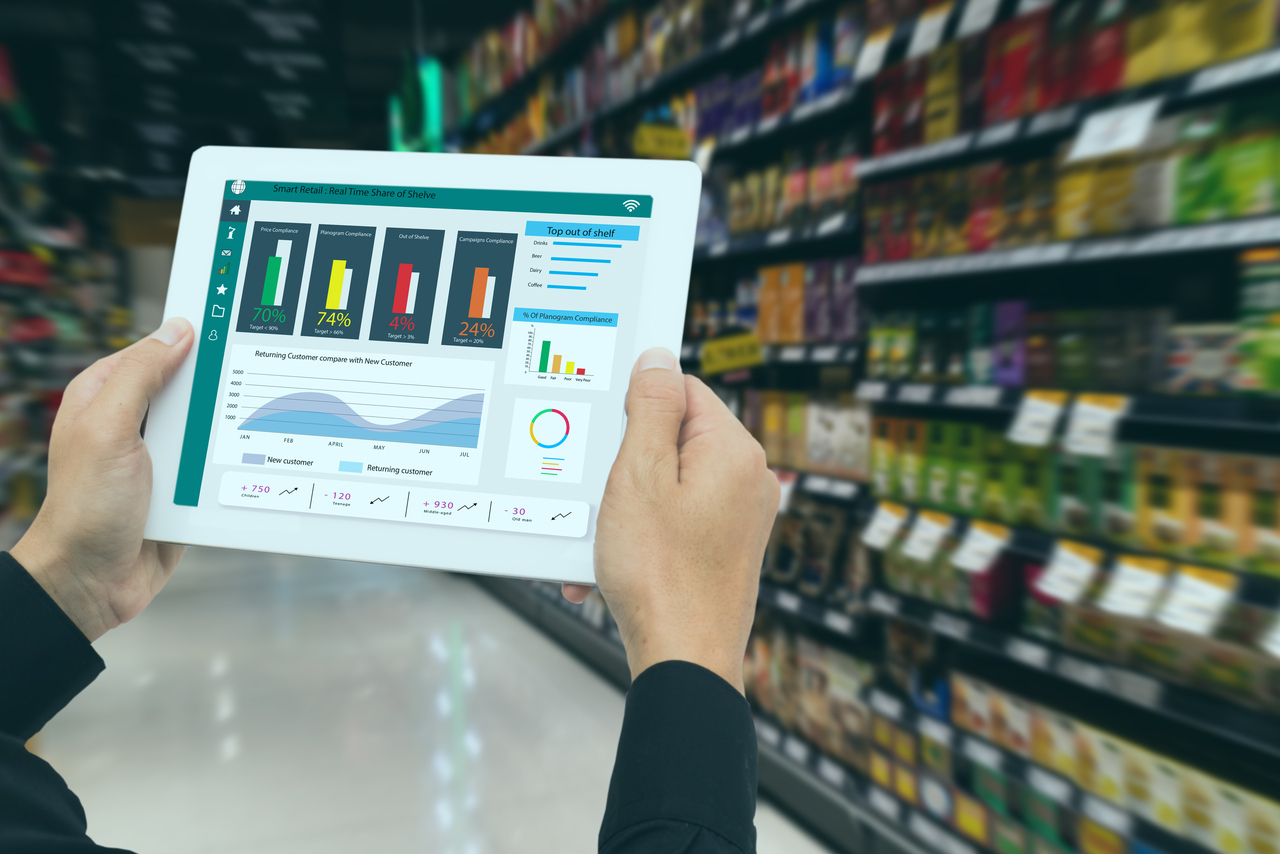
Asset management in blockchain is a prolific way to manage digital assets using blockchain. In order to create a dependable and effective asset management system, key characteristics of blockchain including security, immutability, decentralization, and transparency are being used. Digital assets include security tokens, NFTs, tokenized securities, digital bond etc. The main aim of blockchain asset management is to improve digital asset management’s efficiency, transparency, and trustworthiness. Blockchain asset management systems benefit businesses greatly by providing safe and convenient access to asset data, particularly for real-time asset tracking. Safe and secure architecture of blockchain helps in such a way that only restricted people can change or modify the asset information without malicious intent.
Benefits of Blockchain Asset Management
- Enhanced Security: Every asset on the blockchain is assigned a unique identifier which is unchangeable. This makes sure that assets cannot be spurious. Also, blockchain provides robust encryption making it impossible for unauthorized authorities to tamper with assets.
- Transparency and Trust: In order to make the transaction verifiable for all members on network, the use of blockchain asset management contributes to increased transparency as each transaction is entered on a public ledger. This promotes mutual trust between the parties which is essential for successful financial transactions.
- Cost-effective: By using blockchain, the need of middlemen like notaries or brokers can be eliminated by automating manual tasks which lowers the cost and aids in boosting operational efficiency.
- Traceability: Whenever an asset is passed on to other individual/business, record is kept on blockchain network enabling companies to track their assets and make sure that they are being used for their intended purposes. Also, traceability can assist businesses in recognizing and averting corruption and fraud.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Asset Management
- Asset Custody: Blockchain can be employed for asset custody, offering a tamper-proof and transparent ledger that securely records ownership and asset transfers.
- Wealth Preservation: Blockchain safeguards wealth via a secure, transparent, decentralized ledger. It stores and transfers assets, protecting them from fraud and manipulation.
The transformation of asset management through blockchain is more than a technological shift; it is a paradigm shift. As the technology continues to evolve, asset managers embracing blockchain stand to benefit from improved operational processes, reduced costs while managing assets is more accessible, streamlined, and interconnected than ever before. The future of asset management is undeniably intertwined with the transformative power of blockchain.