Executive Summary
Standardizing control systems is no longer just a technical task—it’s a strategic move to improve operational reliability, reduce lifecycle costs, and unlock return on investment (ROI). This guide examines the business value of standardization, quantifies ROI, and provides a consultancy roadmap for phased implementation.
1. The Need for Control System Standardization
1.1 What Is Standardization?
Control system standardization involves aligning:
– Control platforms (DCS/PLC/SCADA)
– Communication protocols (e.g., OPC UA, Modbus TCP, MQTT)
– Engineering templates (modular logic, HMI faceplates)
– Documentation and compliance frameworks (ISA-88, ISA-95)
It brings consistency across multiple plants, units, or systems—allowing organizations to reduce complexity and optimize resources.
1.2 Market Drivers
– Aging infrastructure
– Cybersecurity requirements (IEC 62443)
– Shortage of skilled workforce
– Pressure to digitize and integrate IT/OT systems
2. Visualizing the Control System Landscape
Here’s a simplified architecture diagram comparing DCS and PLC/SCADA integration paths:
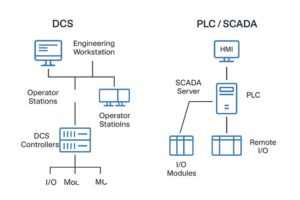
Key Notes:
– DCS typically includes centralized control with native engineering tools and integrated operator stations.
– PLC/SCADA systems are often modular, ideal for discrete or hybrid automation with flexible architectures.
3. Customer Value from Standardization
Operational Efficiency: Common HMIs and alarms reduce operator error and training needs
Engineering Time Savings: Reuse of templates and logic blocks speeds up commissioning
Maintenance & Inventory: Fewer spare parts, unified diagnostics
Compliance & Security: Easier to enforce and audit standards across systems
4. ROI from Control System Standardization
Metric – Typical Savings:
– Engineering & Design – 20–40%
– Training Costs – 30–50%
– Inventory Optimization – 15–30%
– Downtime Reduction – 10–25%
– Energy Efficiency – 5–10%
Case Example: A manufacturing company achieved $1.5M in OPEX savings per year after implementing a global DCS template across three plants.
5. Stepwise Consultancy Guide to Upgrade and Standardize
Step 1: Assess Current State
– Inventory of systems, I/O count, firmware, and architecture
– Identify legacy and non-standard systems
Step 2: Define Target Architecture
– Select core platforms
– Use open communication
– Define reusable libraries and templates
Step 3: ROI-Driven Prioritization
– Build a business case for phased upgrades
– Prioritize by safety, production impact, and support risk
Step 4: Proof of Concept
– Pilot upgrade on a small unit
– Measure KPIs (startup time, alarm handling, MTBF)
Step 5: Standard Rollout
– Develop migration playbooks
– Roll out by criticality or region
Step 6: Continuous Governance
– Set up a Control System Standards Council
– Implement change control and system audits
6. Risk Mitigation Considerations
Risk – Mitigation:
– High Initial Cost – Use ROI-based phased implementation
– User Resistance – Change management and training
– Vendor Lock-In – Open architectures and protocol support
– Legacy Compatibility – Use edge gateways or protocol converters
7. Technologies That Support Standardization
– Control Systems: ABB 800xA, Honeywell Experion, Emerson DeltaV, Siemens TIA/PCS7
– Protocols: OPC UA, Modbus TCP, Ethernet/IP
– AI & Analytics: Standardized data for predictive maintenance and OEE
– Digital Twins: Testing standardized templates before rollout
8. Industrial IoT Imperatives and AI-Driven Assessment
The convergence of Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) through Industrial IoT (IIoT) is driving a paradigm shift in control system standardization. IIoT enables real-time data acquisition, cloud analytics, and remote diagnostics, providing a broader context for standardization efforts.
Key IIoT Imperatives in Control System Modernization:
– **Sensorization:** Expanding the scope of field-level data acquisition for condition monitoring and process optimization.
– **Edge Computing:** Real-time decision-making closer to the asset using edge devices and gateways.
– **Connectivity:** Unified communication across devices using MQTT, OPC UA, and secure VPNs.
– **Cloud Integration:** Scalable storage and analytics for enterprise-wide visibility and benchmarking.
– **Cybersecurity:** Enforcing zero-trust architectures and compliance with IEC 62443/ISA 99.
– **Digital Twin Integration:** Simulating and validating control strategies using live data.
AI-Based Assessment for Value Addition
AI technologies bring a significant leap in value extraction from standardized control systems. By integrating AI-powered analytics, organizations can enhance both strategic planning and operational execution.
AI Use Cases in Standardized Environments:
– **Predictive Maintenance:** Machine learning models detect failure patterns and optimize maintenance schedules.
– **Process Optimization:** Reinforcement learning and adaptive control models reduce energy use and improve yield.
– **Anomaly Detection:** Real-time detection of deviations based on historical patterns using AI algorithms.
– **Quality Control:** Vision and signal-based AI models ensure consistent product quality.
– **Root Cause Analysis:** NLP-driven analysis of alarms and operator logs for faster troubleshooting.
– **Automated Reporting:** AI streamlines compliance and audit reporting using real-time data aggregation.
By embedding AI into the standardized architecture, companies unlock continuous improvement loops, reduce downtime, and move from reactive to predictive operations—maximizing ROI while ensuring resilience.
8.1 Case Study: AI-Augmented Control System Standardization in a Steel Plant
A mid-sized steel manufacturing company undertook a phased control system standardization across its four production units. The project involved migrating from a mix of legacy PLCs to a unified DCS platform with IIoT gateways and OPC UA connectivity.
The company integrated AI-based analytics into their standardized system to enable predictive maintenance and process optimization. By deploying machine learning models at the edge and using cloud-based dashboards, they were able to identify asset degradation trends and optimize combustion parameters in real time.
**Results:**
– 18% reduction in unplanned downtime
– 12% improvement in fuel efficiency for reheating furnaces
– ROI achieved within 14 months due to reduced maintenance and improved yield
– Operators adapted more easily due to standard HMIs and AI-assisted diagnostics
**Why AI Is Central to Point 8:**
AI complements Industrial IoT by transforming raw operational data into actionable insights. In the context of standardization, AI enables real-time optimization, anomaly detection, and continuous improvement, turning the standardized infrastructure into a dynamic, self-learning ecosystem.
9. Conclusion: Standardization as a Strategic Enabler
Control system standardization is not about “one size fits all”—it’s about scalable design, predictable operations, and business continuity. When approached stepwise with a clear ROI roadmap, it becomes a key enabler for digital transformation and sustainability
📌 Call to Action
Thinking about a control system upgrade or rationalization? Start with a baseline assessment and let us help you build a stepwise, cost-effective standardization strategy.