As industries progressively adopt AI, machine learning (ML) and Generative AI (GenAI), Operational Technology (OT) is also undergoing a gradual but profound transformation. These advanced technologies are reshaping industrial operations, with their impact becoming particularly evident in the field of Industrial Automation. While digitalization efforts have been evolving over the past few years, the transition towards IT-OT convergence marks a critical milestone in this journey. However, this integration also introduces several challenges, with high security risks and the potential for control system failures being the most prominent concerns.
Though the OT team is playing an essential role in ensuring smooth operations, yet many industries face ongoing obstacles that hinder efficiency across the entire OT project lifecycle. This highlights the pressing need for technologies that can proactively identify security threats, predict potential failures, and ensure continuous support for OT professionals to maintain high availability and operational excellence.
The complexity of these challenges deepens as interdependencies between the various issues grow, which in turn increases system vulnerabilities and downtime risks. Below are some of the key challenges OT personnel face in their day-to-day operations:
Challenges
1. Troubleshooting PLC/SCADA Issues
Diagnosing and resolving PLC/SCADA issues without a structured troubleshooting approach often leads engineers to spend excessive time identifying faults, causing production delays.
2. Lengthy and Complex Control Write-ups
When control write-ups are too lengthy and complex, pinpointing the root cause of the problem becomes time-consuming. Engineers struggle to extract actionable insights quickly, resulting in prolonged downtime.
3. Time-Consuming in resolution of recurring Control issues
A lack of historical failure data, predictive analytics, automated troubleshooting, resolving recurring control issues becomes more difficult and time-consuming.
4. High effort in Engineering drawings and Report Generation
Manually creating control documents, CAD drawings, compiling engineering reports from multiple sources are time-consuming and error prone.
5. No early warning signs for failures
Many organizations lack a well-defined process for maintaining OT systems resulting in inefficiencies, missed updates and increased vulnerabilities.
6. Lack of support due to knowledge gap
OT teams often rely on a small group of experts for troubleshooting and maintenance. When key personnel take unplanned leave, their absence creates significant disruptions.
The challenges listed above are not an exhaustive list and may not be a direct fit in every case.
Addressing these challenges requires a mix of automation, process standardization and AI-driven insights to enhance efficiency and reduce downtime of the production systems.
For a major Petrochemical Industry, we have implemented AI and GenAI technologies to address maintenance-related challenges specifically faced by maintenance personnel. By contextualizing production and maintenance data, time series data, and engineering data, we’ve seen significant improvements in addressing these challenges. Leveraging this thought, we have been expanding our efforts across various dimensions, as shown in the image below, to demonstrate how these technologies can effectively address the challenges faced by OT professionals.
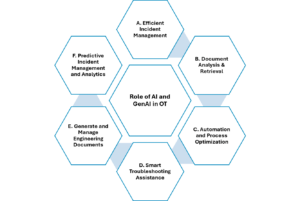
Dimension
A. Efficient Incident Management
· Provide efficient recommendations for known control system issues by leveraging pretrained models (Network issue, Integration issue etc)
· Smart notification prioritization ensuring the right level of urgency is assigned to each issue
· Automate the recurring and access related issue and approval cycles
Benefits
· Reduces the incident response time.
· Improving system uptime.
B. Document Analysis & Retrieval
· Analyze Control drawings, Wiring, P&ID diagrams, Control Writeup for insights
· Quick retrieval of (Engineering drawings, Technical manuals, Datasheets, SOPs etc)
Benefits
· Improved decision-making by analyzing documents for insights.
· Increased efficiency with quick retrieval of documents streamlines work processes.
C. Automation and Process Optimization
· Auto Control Code generation based on Control write-up
· Auto generate configuration files for PLC/RTU
· Automated Software Testing
Benefits
· Reduces time and efforts for control code development.
· Increases consistency and accuracy in code.
D. Smart Troubleshooting Assistance
· Assist in diagnosing and troubleshooting control code issues.
· Guided resolution steps based on documentation
· Fault Diagnostics with Root Cause
Benefits
· Reduces production downtime
· Improves reliability of control systems by predicting potential issues in the control code.
E. Generate and Manage Engineering Documents
· Auto generate BOM and Engg. Drawing from P&ID, Version control
· Create Control Strategy Documentation
· Automated Report Generation- FAT, SAT
· Process documentation & Compliance
Benefits
· Increases efficiency by automating the creation and management of engineering documents
· Improve accuracy by minimizing human errors.
F. Predictive Incident Management and Analytics
· Threat Detection and Anomaly Detection – OT Security, OT Network
· Control code analysis to identify coding errors, inefficiencies using AI driven predictive tools.
· Critical Control System hardware Performance analysis (Processor/CPU utilization, Memory usage, Communication Network performance)
Benefits
· Enhanced operational efficiency by predicting potential issues in assets and control systems.
· Improved Security by identifying potential security threats and anomalies in OT networks.
However, it is important to note that, since these technologies are controlling critical production systems, we cannot rely entirely on them without human involvement for validation and approvals. Directly integrating with the OT application remains a point of risk, particularly when it comes to downloading changes directly into live production operations. While this presents a challenge, we can still leverage these technologies to enhance operational efficiency, provided proper safeguards are in place.
In conclusion, the ability to mitigate these challenges is essential for achieving improved operational effectiveness. By embracing newer technologies and data-driven approaches, we can significantly reduce the impact of challenges throughout the entire lifecycle of an OT project, ensuring better control, security, and decision-making.