In today’s digital age, mobile applications on platforms such as Apple iOS and Android have become integral to our daily lives. These applications keep us connected to social media, banking, chatting, video calling, news, and much more. However, have you ever wondered how mobile phones manage to run multiple applications simultaneously, enable chatting or calling without an internet connection, and maintain battery life for more than a day?
While efficient chipsets contribute to faster processing, the key to optimizing battery usage when multiple applications are sharing a phone’s resources lies in the implementation of push notifications. Push notifications are a reliable and efficient method for applications to connect with end users and enhance engagement.
In this blog, we will delve into the reasons behind the effectiveness of push notifications, explore the different formats they come in, and discuss the benefits of implementing push notifications in mobile applications. The push notification service was introduced in Apple iOS 3 and Android 2.2 versions, revolutionizing the way applications interact with users.
Why Push Notification
- App development picked up
There was sudden jump in the mobile app development. Many apps simultaneously competing for CPU and Memory of the device - Battery usage
Devices ran out of battery faster due to apps being always active
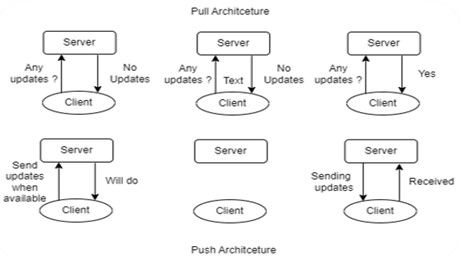
Push Vs Pull Technology
Push and pull technologies are two different ways of transferring data between a client and a server. In pull technology, the client requests data from the server, and the server responds with the requested data. In contrast, in push technology, there is a paradigm shift where server sends data to the client without the client requesting it.
For example, email uses push technology whereas opening a webpage uses pull technology.
The Benefits of Push Notification
- Reduced Server load: Sends data to client if data has changed since last update. Help with the scalability of applications as the server can cater to more users and load.
- Better User Management: Users are provided with relevant information and in real time. This helps users to be engaged with applications and improves customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Latency: Data is sent to the client without the client requesting it and hence there is no delay in receiving data.
- Prioritized Notification: VoIP Call Notification are sent with higher priority and immediately shown on device. Messages and data updates are sent with lower priority.
- Lesser Device Resource Utilization: Applications go to an inactive state when in background mode which reduces resources utilization and in turn saves the battery usage.
- Multi-Device Reach and easy Integration: Push notifications can be sent across multiple devices and across platforms, making it easy to reach your device wherever they are. For example, the same application is running on Apple iPhone and iPad, both devices get instant notification. Similarly, if the same application is running on Apple iPhone and an Android mobile device, both devices get instant notification.
APNS / FCM Solution on Apple iOS / Android devices for enterprise telephony
The following details will explain how APNS / FCM solution works for Enterprise Calling application running on mobile devices.
- Enterprise Telephony – Provider Application Server
- APNS – Apple Push Notification Service
- FCM – Firebase Cloud Messaging
- PNS – Push Notification Service
- Endpoints – Physical VoIP IP phones, soft clients
How it Works: PNS
- Provider Application & Device Connection
The provider application (e.g. enterprise telephony soft clients) sends a request to Push Notification Service (APNS or FCM) to receive a device token for each user who has enabled push notification on their device and this device token is stored in the Provider Server. - Provider Sends Notification to PNS
The provider Application server sends the message payload and device token to Push Notification Service (APNS or FCM). - PNS Delivers Notification
PNS sends the notification to the user’s device after doing its necessary security validations using the device token and the message payload. - User Sees Notification
The user gets a banner or alert notification on their device and can choose to act or dismiss the notification.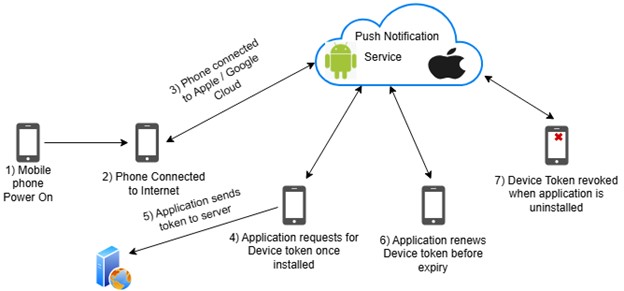
Fig 2 – Device Token Flow for Mobile Application 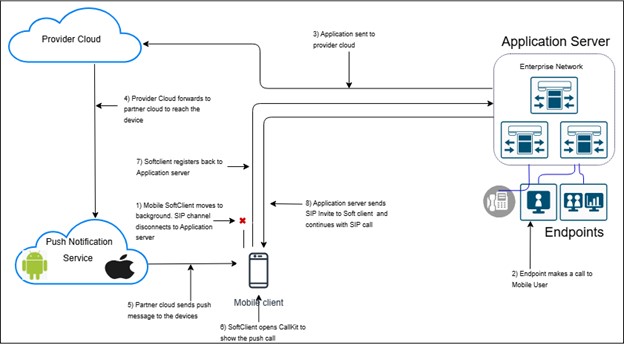
Fig 3 – VoIP Call Push Flow for Enterprise telephony Application on Apple and Android Phones
Cloud Push notifications have significantly contributed to the exponential growth of the application market, while ensuring minimal resource usage on mobile devices. However, there is a critical consideration: what happens when the internet is unavailable or when users are in areas with no internet connectivity?
For regular users, delayed information may not pose a significant issue. However, in scenarios such as hospitals where nurses need to urgently communicate with doctors, or on cruise ships where internet access may be limited, the lack of timely notifications can be problematic. To address these challenges, an alternative form of push notification was envisioned.
Drawbacks of Cloud based PNS
- Internet connectivity
Devices need to be connected to the internet constantly; else they will miss notifications. This will be still acceptable for messages or data but will not work for time sensitive applications like enterprise telephony calls. - Infrastructure / firewall
Enterprise customers need to update the network infrastructure with necessary firewall rules to allow internet for PNS. Firewall rules need to be updated based on new servers capable of sending push are added / changed across the globe. - Internet restrictions
With many global security threats on the internet, Enterprise customers do not want to enable internet on their network. Stringent privacy laws in Health care industry imposes restrictions on internet. Certain environments like Airplane, Cruise ships, Military establishments do not have internet, and all push notifications will fail.
Local Push Notification
Considering the drawbacks of Cloud based PNS Push, Apple came up with a new way of Push Notification called Local Push Notification. It was introduced in iOS 14. This new mechanism eliminated the drawbacks of APNS. Customers have options now for push notification based on the deployment scenario. They could have APNS only, LPNS only or LPNS + APNS. Android devices also have Local push notification which can be used for location-based applications, offline reminders etc. but it cannot be used for VoIP calls as persistent service monitoring events when applications go to background does not exist. Apple’s iOS maintains a lightweight service which can monitor a few standard protocols like TCP, webRTC, WebSocket etc. push messages to corresponding application and wake them up.
- Wi-Fi Setting
Apple devices need to know which Wi-Fi is allowed for Local Push Notification. This can be manually set from the device or configs pushed down to the device from the server - Local Push Extension
Local Push extension will become active whenever the device is connected to the Wi-Fi which is marked for Local Push Notification. The extension will initiate a persistent connection to the server post the security posture verification. Through this persistent connection, the server will send the push message whenever a notification / call needs to be presented to the device. The device will wake up the application and show the notification / call and user can take necessary action.
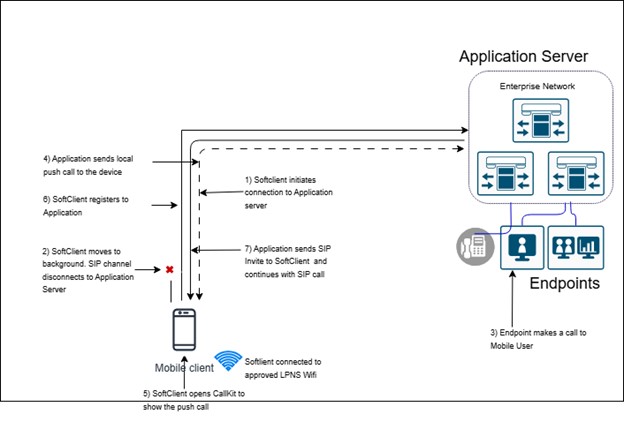
How it Works: Local Push Notification Service with Enterprise telephony
- Apple iOS
Apple devices enable a local push extension whenever the device is connected to approved LPNS Wi-Fi. - Application Connectivity information
Connectivity information for local push is sent to the mobile application post login. Application initiates a persistent connection to server when device connects to approved LPNS Wi-Fi. - Push Notification
Server sends the push notification to the user’s device using the persistence connection. - User Sees Notification
The user gets a banner or alert notification on their device and can choose to take action or dismiss the notification.
Feature comparison of Enterprise Telephony
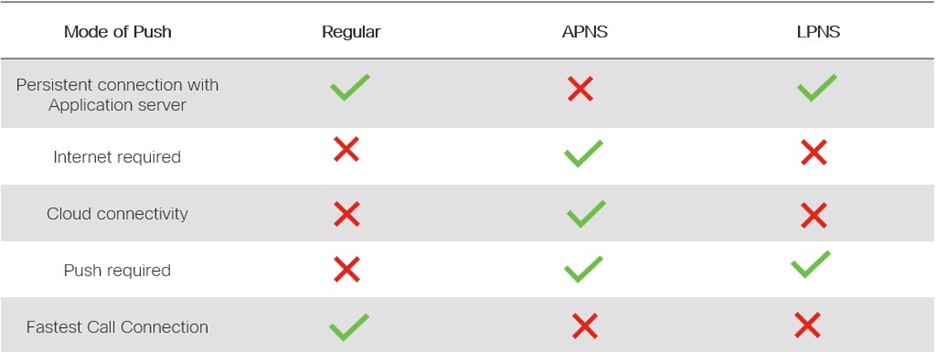
Note: Regular (SIP Registered), Traditional persistent connection of SIP channel between Application and Server. Consistent Keepalive messages to keep the persistent connection intact is a big drain on battery capacity.
Future trends for Push Notification
- Enhanced Security for threat Management:
Since the data for push message traverses from server to push notification cloud and then back to Apple or Android device, it becomes imperative to have it secured with the latest encryptions to avoid potential threats - Use AI to summarize notifications
Apple is working on summarizing the notification alert and rendering a prioritized list. Users can act based on AI’s inputs. This will be very useful in scenarios where too many notifications are received, and user needs to scroll to view all the notifications. - Notification controls
More granular controls on the notification alerts. This will enhance user personalization and avoid unwanted interruptions. - Broadcast notification
This new notification method could be used in scenarios where multiple devices need to get an update of an event, news etc. Instead of the server doing 1:1 push notification to every device which is subscribed, broadcast notification uses a channel where all devices are subscribed to and when an update is posted, PNS channel will send the update to all devices subscribed for that event. - Seamless data transfer
Similar devices can create an internal network using the same Wi-Fi, NFC, Bluetooth, Infrared, certain audio frequencies etc. use Local Push services to transfer data 1:1 or 1 to many. Apple iPhones has a local Send option to send data across iPhones whereas Huawei uses hand gestures and AI to transfer data without even the need to connect to a common connection protocol.
Closing thoughts
In conclusion, push notifications have revolutionized the way mobile applications interact with users, providing timely and relevant updates that enhance user engagement and optimize resource usage. The Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) has been instrumental in this transformation, offering a robust and reliable platform for delivering notifications to iOS devices.
However, the limitations of internet connectivity have highlighted the need for alternative solutions. Local Push Notification Service (LPNS) addresses these challenges by enabling notifications without relying on an active internet connection. This innovation ensures that critical information can be delivered in scenarios where connectivity is compromised, such as in hospitals or remote locations.
By leveraging both APNS and LPNS, developers can create applications that are not only engaging but also resilient to connectivity issues, greater security to minimize data losses in transit and ensuring users receive important updates regardless of their environment. As the mobile application market continues to evolve, the role of push notifications will remain pivotal in driving user engagement and enhancing the overall user experience.