Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that enhances real-world objects by adding computer-generated information, graphics, and sounds, thus enhancing the perception of the real world. From a discrete manufacturing perspective, AR is used to visualize, monitor, and control the manufacturing process in real-time, leading to improved efficiency, quality, and safety.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality:
Augmented Reality differs from Virtual Reality (VR) in that AR blends virtual information with the real-world environment, whereas VR immerses the user in a fully virtual environment. Augmented Reality is more suitable for the manufacturing industry as it allows the user to stay engaged with the physical world while augmenting it with relevant information.
Practical Applications:
The manufacturing industry has been quick to adopt AR technology due to its practicality and ability to provide real-time assistance to the workforce. Some practical applications of AR in manufacturing are:
- Training and Education: AR technology can provide an interactive and immersive training experience to new employees, enabling them to learn quickly and efficiently. Jaguar Land Rover, for example, uses AR headsets to train their employees in assembly line processes.
- Maintenance and Repair: AR can be used to provide real-time assistance to maintenance and repair personnel, helping them diagnose and fix issues more quickly. Boeing, for example, uses AR headsets to assist their technicians in wiring harness installation.
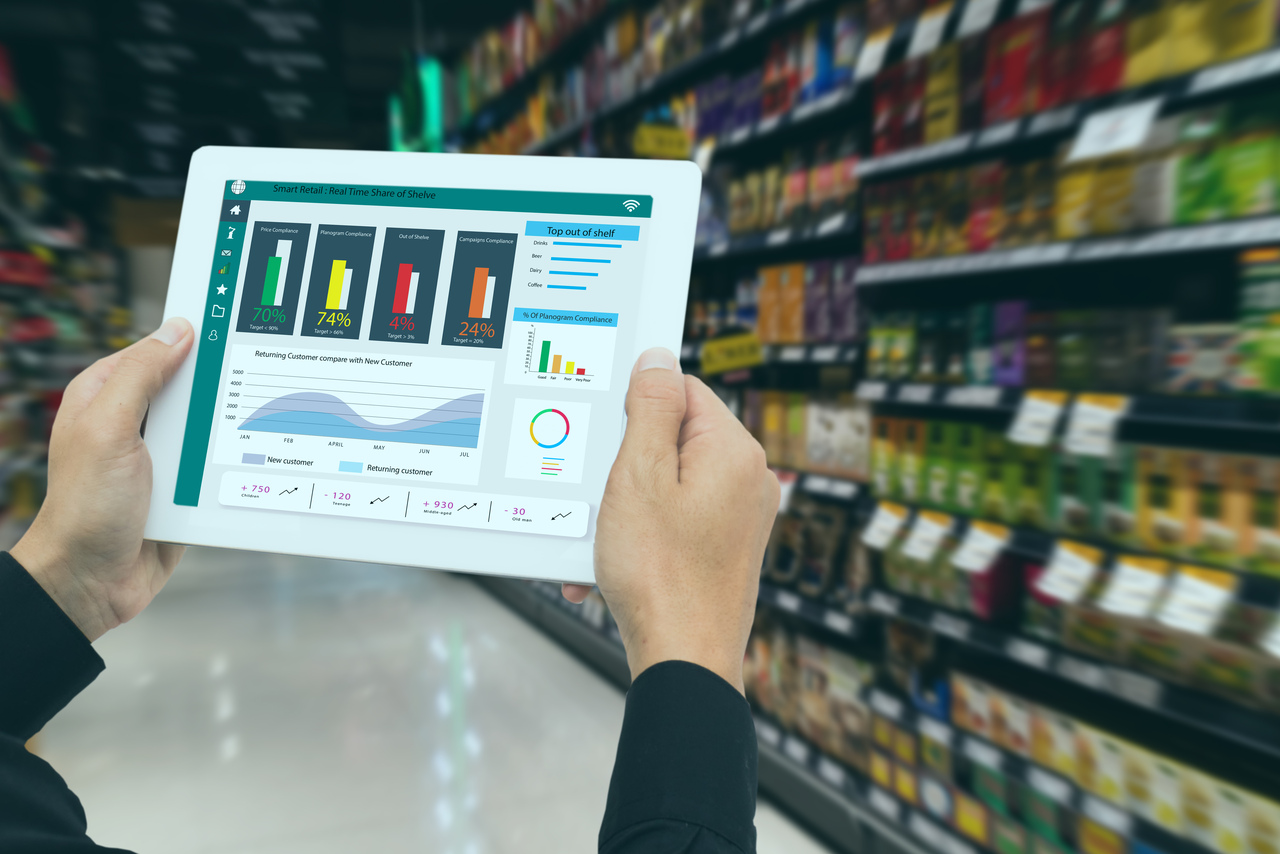
- Quality Control: AR can be used to visualize and monitor the manufacturing process in real-time, leading to improved quality control. Volvo, for example, uses AR technology to visualize and test car designs in real-time.
- Remote Assistance: Using AR glasses and mobile devices, the experts can provide real time guidance the onsite workers, by overlaying digitally the instructions and annotations and visual cues in the real world thus enabling smooth troubleshooting.
- Ergonomics and Safety: While using the AR technology, the workers can leverage the guidance via the onscreen text, annotations / voice w.r.t to their posture and the method to handle the equipment so that the work happens in an efficient way while giving utmost importance to workers safety.
Augmented Reality Probable Use Cases in Industry 5.0:
Industry 5.0 is the next phase in the evolution of the manufacturing industry, where humans and machines work together in a harmonious and collaborative environment. Augmented Reality technology is likely to play a significant role in Industry 5.0, with the following probable use cases:
- Collaborative Robotics: AR technology can be used to enhance the collaboration between humans and robots in the manufacturing process, leading to improved efficiency and safety.
- Real-time Data Visualization: AR technology can be used to provide real-time data visualization to the workforce, enabling them to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
- Predictive Maintenance: AR technology can be used to monitor the manufacturing process in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Conclusion:
Augmented Reality technology is transforming the manufacturing industry by enhancing efficiency, quality, and safety. As the manufacturing industry moves towards Industry 5.0, the role of AR technology is likely to become even more significant, with increased collaboration between humans and machines and real-time data visualization. The manufacturing industry needs to embrace AR technology to stay competitive and achieve better outcomes.