Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary tool that can greatly enhance the security, transparency, and traceability of various business processes. When integrated with Oracle ERP Cloud, this technology offers immense potential for transforming the way organizations operate. The integration can be achieved using Oracle Blockchain Platform or other third-party blockchain solutions. By leveraging the power of blockchain, businesses can ensure the integrity of their data, streamline operations, and foster trust among stakeholders. This combination presents a unique opportunity to unlock new levels of efficiency and effectiveness in the realm of enterprise resource planning.
Some use cases include:
• Supply Chain Management: Enhance visibility, traceability, and data integrity across the entire supply chain by securely storing and sharing information about products, shipments, and transactions.
• Smart Contracts: Automate contractual agreements and business processes through self-executing contracts, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency.
• Procure-to-Pay: Improve transparency and reduce fraud risk in procurement by validating supplier credentials and tracking transactions on an immutable ledger.
• Financial Management: Streamline financial transactions, such as intercompany transfers, by automating reconciliation and settlement processes on a shared ledger.
• Compliance and Audit: Enhance regulatory compliance and audit processes by providing a transparent, tamper-proof record of transactions and data.
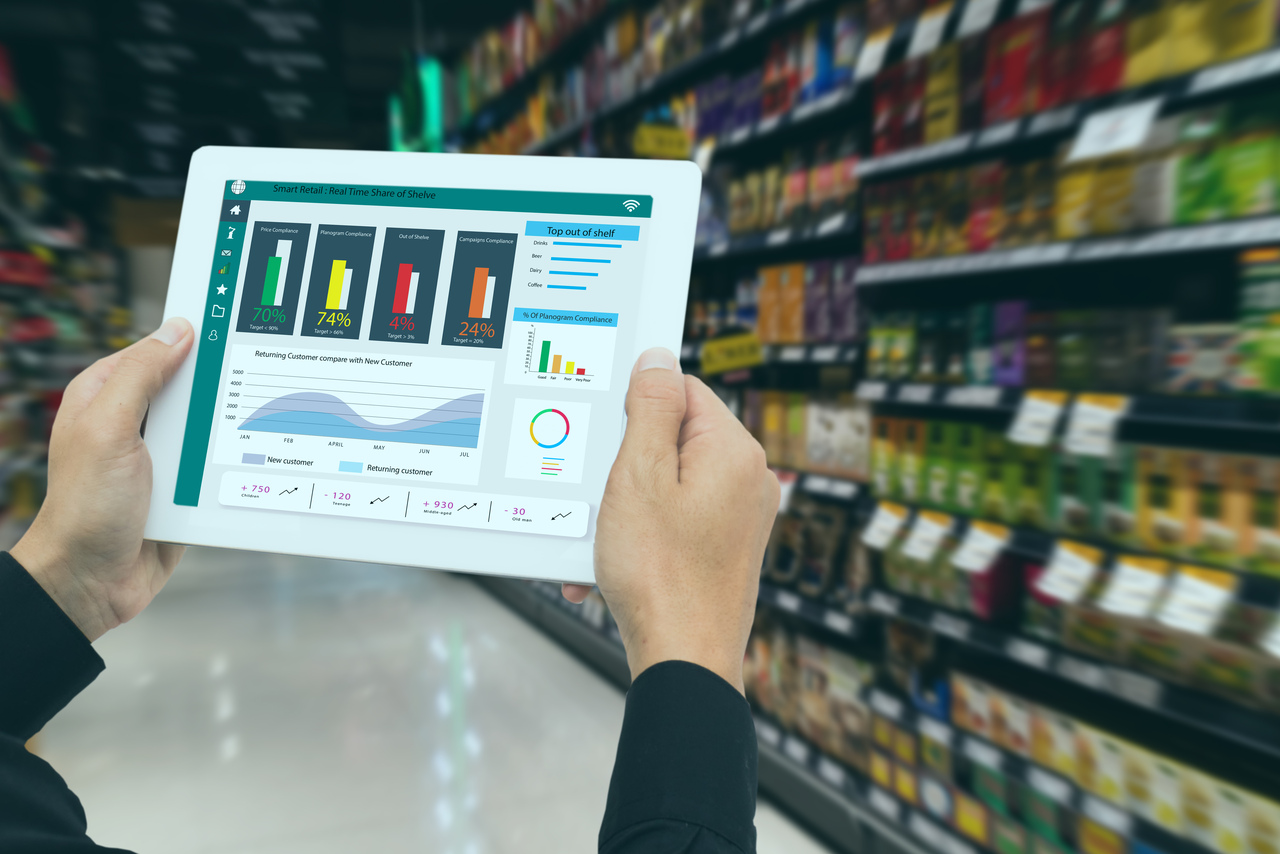
Blockchain technology can revolutionize the pricing process of Oracle’s order management system by providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to track and manage pricing data.
By leveraging blockchain-based smart contracts, businesses can automate the pricing process and ensure transparency and accuracy. These smart contracts can be programmed with specific rules and conditions that determine prices based on factors like supply and demand, competition, and market conditions. This integration enhances security, transparency, and traceability, providing real-time visibility into pricing updates and eliminating the risk of tampering or fraudulent activities. It introduces a new level of efficiency and effectiveness to the pricing process, fostering trust among stakeholders and improving overall business operations.
Another way that blockchain could be used in the pricing process is through the use of tokenization. Tokenization is the process of representing physical assets, such as products or services, as digital tokens on a blockchain. By tokenizing the products and services offered in the Oracle order management system, the prices can be determined by the market demand for the tokens, rather than being set by the company.
Using blockchain in this way can bring more transparency and trust in pricing process and also help to reduce fraud and errors in the order management process.
There are several advantages present for using blockchain technology in the pricing process of Oracle’s order management system:
• Transparency: Blockchain technology provides a transparent and tamper-proof record of all transactions, making it easy to track and verify pricing information.
• Automation: Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate the process of setting prices, making it faster and more efficient.
• Decentralization: By using blockchain technology, the pricing process can be decentralized, which in turn will allow multiple parties to access and update pricing information, which can improve the accuracy and timeliness of pricing information.
• Tokenization: Tokenization allows for the creation of digital assets that can be traded on a blockchain network; this can help to determine prices based on market demand for the tokens.
• Data Security: Blockchain technology provides a secure method for storing and sharing data. This can help to reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure that pricing information is only accessible to authorized parties.
• Traceability: Blockchain allows to track the origin of the product and services which can be used to determine the prices.
• Cost Savings: Automating the pricing process using blockchain technology can reduce the cost of manual labor and the risk of errors.
• Immutable record: Blockchain’s immutability feature allows to have an unchangeable record of the pricing process, which can help in auditing and compliance.
• Interoperability: Blockchain can enable different systems to interact with each other, allowing for greater efficiency and automation in the pricing process.
It’s important to note that, while blockchain technology can bring a lot of benefits in the pricing process, it might not be a perfect fit for every situation. The implementation and usage of blockchain technology should be evaluated based on the specific use case and requirements, and the potential benefits should be weighed against the costs and complexity of implementation.
There are a few steps that could be taken to use a blockchain-based smart contract to automate the process of setting prices for products and services in Oracle Order Management Cloud. Here’s an example of how it could be done:
• Identify the products and services that will be offered on the Oracle Order Management Cloud.
• Develop a smart contract that specifies the rules and conditions that determine the prices for each product or service. The smart contract could consider factors such as supply and demand, competition, and market conditions.
• Integrate the smart contract into the Oracle Order Management Cloud system. This can be done by connecting the Oracle system to a blockchain platform (e.g. Ethereum) that supports smart contracts.
• Deploy and upload smart contract to blockchain network for pricing.
• When smart contract is deployed, there are ways to automatically set prices for products and services based on the rules and conditions specified in the smart contract.
• Implement a mechanism for updating prices on regular basis as market conditions change, such as through oracles, which are smart contract enabled connectors.
• Monitor the performance and adjust the smart contract if required, so that pricing is aligned to business goals.
It’s important to note that this is just one example of how blockchain-based smart contracts could be used to automate the process of setting prices for products and services in Oracle Order Management Cloud, and the specifics of the implementation will depend on the specific use case and requirements.