Role of CMMS in Wind Farm Maintenance
Since O&M [Operations and Maintenance] costs are very high for wind turbines and also cost of wind turbine components & installation charges are significant; it is very critical to extract optimal value from wind turbines. A large number of wind turbines are installed together in a farm and thousands of components are involved with each turbine further increases the complexity. It is virtually impossible to manage the assets manually and maintain them at optimal performance at this scale. Therefore, a CMMS [Computerized Maintenance Management System] is a must to manage the wind farm and its large number of assets and subassemblies. A variety of CMMS solutions are available which offer a wide range of functions including planning, scheduling, assigning, monitoring, controlling, reporting and other related administrative functions, for effective and efficient management of maintenance.
Myth 8: Wind turbines doesn’t need a specialized CMMS software solution because of their simple maintenance requirements
Involvement of complex assets requiring asset configuration management, integration with Operations Technology [OT] to process real time sensor data, stringent qualifications/safety requirements, reliable preventive maintenance and use of digital automation, IoT [Internet of Things], AI/ML [Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning], Asset Analytics to power a reliable predictive maintenance necessitates a specialized CMMS software solution.
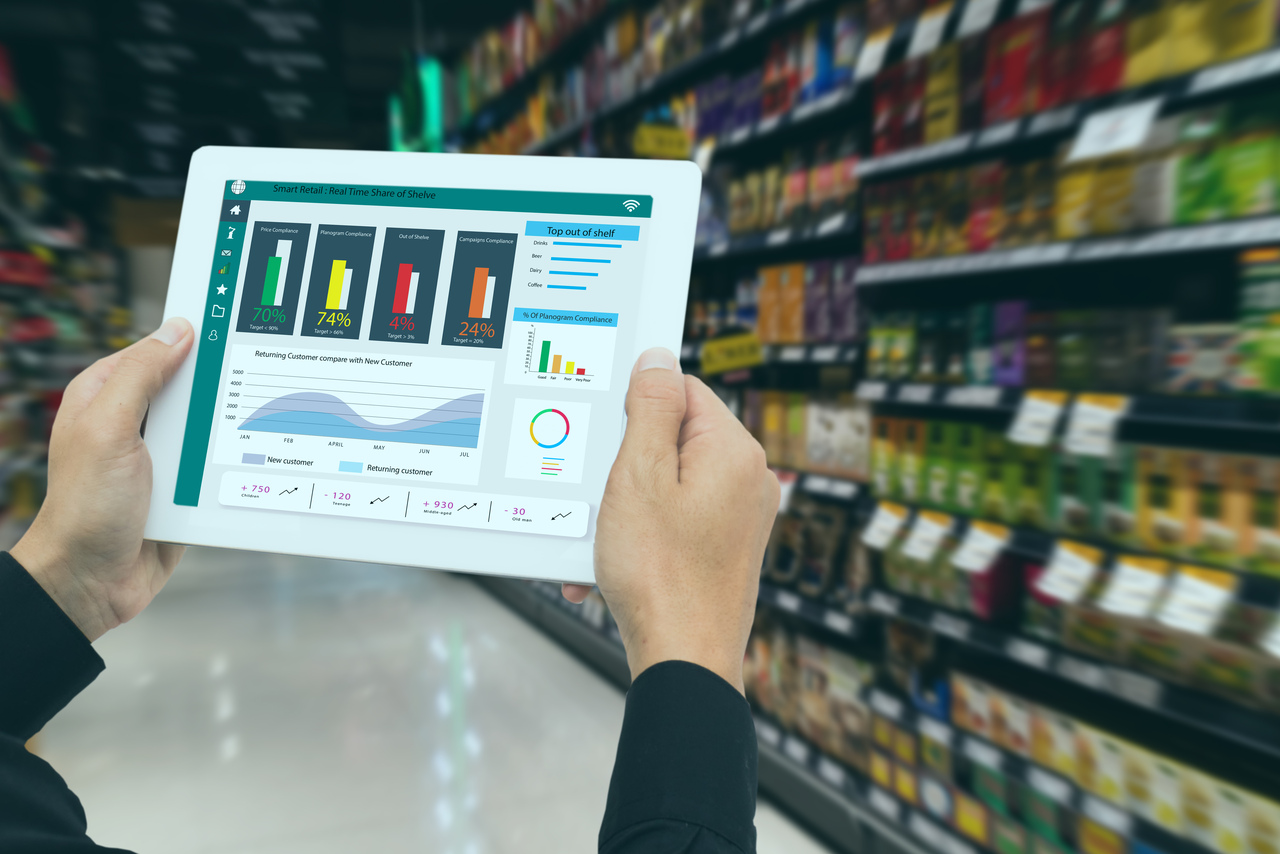
Below picture depicts the role of Operations Technology [OT] and CMMS for managing a wind farm:

Sensors installed on the wind turbines send signals about operational performance to the SCADA [Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition] server for real time monitoring. Relevant data from SCADA server is extracted and sent to CMMS server. Condition alerts setup in the CMMS server trigger a Corrective Maintenance work order. In parallel, time or meter based Preventive Maintenance work orders can be setup in CMMS based on wind turbine OEM guidelines to trigger a Preventive Maintenance work order. In the long run, data generated could be analyzed using AI/ML/Advanced Analytics to derive insights which can lead to Predictive Maintenance increasing the overall reliability and reducing the maintenance cost.
Some key business functions supported by CMMS software solutions in the context of wind farms are listed below:
- Components (Parts) Management: Maintaining the spare parts inventory is extremely critical because any downtime of wind turbines directly affects revenue generation. Therefore, parts availability for replacements and repairs is very critical. At the same time, some of the parts involved are very specialized and expensive, so maintaining optimal inventory level of parts is important for cost effectiveness and service reliability. Efforts should also be made to reduce the lead time for the parts and increase vendor reliability.
- Assemblies Management: Around 8000 various components come together to form a complex sub-assemblies and assemblies to make a large wind turbine. Maintaining an accurate assembly structure is an important function with the flexibility to assemble and dissemble as needed
- Asset Management: Tracking the life cycle of wind turbines and critical spares from purchase, commissioning, maintenance to retirement and disposal; and while doing so tracking the cost information like cumulative maintenance cost and replacement cost to make informed decision on repair vs replace
- Managing Third Party Service Providers: External contractors could be involved in the maintenance of the wind turbines given that it requires specialized skills. So, defining appropriate contract terms with them for maintenance is critical including the appropriate SLAs [Service Level Agreements]
- Crafts/Qualifications/Certifications: Wind turbines are specialized engineering equipment and require skilled technicians to maintain them. Maintaining a list of crafts/skills, qualifications and certifications for internal crew and external contractors is very important from compliance perspective
- Maintenance Tools & Equipment: Wind turbine maintenance requires specialized tool and equipment so keeping appropriate inventory of required tools in stock in pristine conditions is important
- Safety Clearances: Wind turbines typically operate at a very high altitude involving heavy mechanical components and electric components, therefore there is an inherent heavy risk in maintenance. Therefore, applying appropriate safety prerequisites is of utmost importance before and after maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance: The installed wind turbines come with preventive maintenance [PM] instructions from the OEM. All these PM tasks and schedules need to be managed well for timely maintenance and ensuring maximum asset life
- Work Management: Work Orders needs to be planned for wind turbines inspection, repair, and maintenance. Then they need to be scheduled, assigned to crew, and facilitate for capturing work execution details including any observations and failure details for future analysis
- Predictive Maintenance: Since the logistical challenges with wind turbine maintenance are high and the downtime impacts revenue, a more reliable and data driven predictive maintenance is critical to reduce downtime, maintenance cost while enhancing asset availability and asset life. Modern CMMS systems can play a big role in this
- SCADA integrations: Wind turbines come with a lot of sensors which are constantly generating a lot of data. So, the CMMS system should be able to easily integrate with the SCADA system to capture the sensor generated data and process them to generate appropriate alerts and work orders as needed
- Geographical Spread Asset: Appropriate location tracking and map view of all the assets helps to track them, a GIS system is very helpful for this
- Mobility: The maintenance of critical part of wind turbines happens at steep heights. To maximize productivity, it is of utmost importance that all the details of work order and asset are available to the technician on an easy to use Mobile device, with the ability to easily capture the work execution details.
The CMMS solutions should support some or all above functional requirements. Some of the CMMS solution options include IBM Maximo, eMaint, Infor EAM, CHAMPS, Microsoft Dynamics, SAP EAM, UpKeep among others.