Cybersecurity has become a decisive factor in acquisition success. Overlooking cyber risks can erode deal value, damage reputation, and trigger regulatory penalties.
This blog outlines critical challenges, hidden vulnerabilities, compliance pitfalls, and cultural misalignment—and introduces a phased Secure acquisition Lifecycle Framework, from Pre-Day 1 through Operate, to safeguard integration and preserve enterprise value. Cyber due diligence must be treated as a strategic lever, not a technical checkbox, for achieving successful acquisitions.
Introduction
Acquisitions drive growth and market expansion, but they also introduce significant cybersecurity risks. Integrating two distinct technological ecosystems and governance models creates vulnerabilities that attackers actively exploit.
Cybersecurity is no longer a technical detail—it is a strategic imperative for protecting deal value. A proactive, risk-based approach during due diligence and integration is essential to ensure resilience and prevent costly disruptions.
Real World Lessons
- UnitedHealth Group and Change Healthcare (2024): ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware exploited MFA gaps compromising 100M+ health records and causing major operational disruption.
- Marriott & Starwood (2018): Undetected breach exposed 500M guest records, resulting in £18.4M GDPR fines and lawsuits.
- Under Armour & MyFitnessPal (2018): Credential theft exposed 150M user accounts (emails, hashed passwords) after hackers accessed MyFitnessPal’s database post-acquisition.
Key Insights:
- You acquire the target’s history, not just its future.
- Cyber risk doesn’t pause for integration—security must lead, not follow.
- You’re not just buying assets; you’re inheriting liabilities and latent threats.
Cybersecurity Challenges in Acquisition
Acquiring a company means inheriting its attack surface. Common challenges include:
- Legacy systems and outdated controls: Old infrastructure creates exploitable gaps.
- Misaligned security policies: Conflicting standards weaken governance.
- Third-party and supply chain risks: Vendor dependencies introduce hidden threats.
- Integration under time pressure: Accelerated timelines increase misconfigurations.
- Cultural differences in security practices: Divergent approaches hinder consistent enforcement.
These factors increase vulnerability during and after acquisition. Embed security across the acquisition lifecycle to reduce vulnerabilities and ensure compliance.
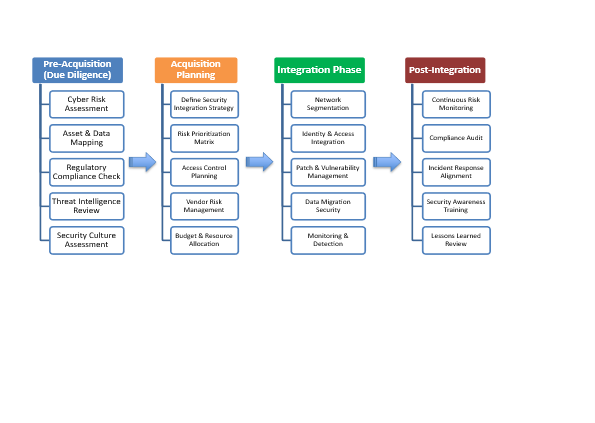
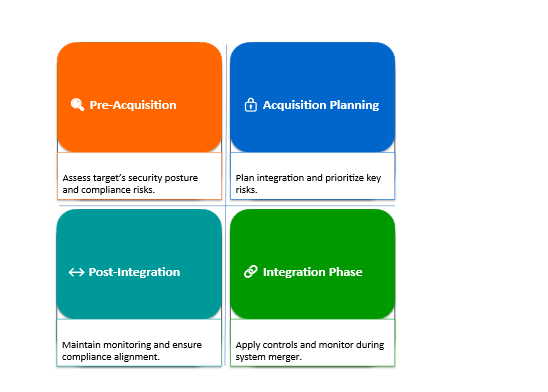
Secure Acquisition Lifecycle Framework
Four pillars guide secure integration:
Approach for Acquisition Timeline
1. Phase 1: Pre Acquisition – Day 1: Due Diligence & Planning
2. Phase 2: Day 1: Acquisition Planning
3. Phase 3: Days 1–100: Integration
4. Phase 4: Post Integration (Operate)
Benefits obtained
1. Early Cyber Due Diligence → Prevents costly surprises by identifying security and compliance gaps before deal closure.
2. Legacy System Risk Awareness → Reduces breach likelihood by proactively addressing exploitable vulnerabilities.
3. Phased Integration → Ensures smoother IAM and network security alignment, minimizing disruption.
4. Continuous Post-Close Monitoring → Maintains resilience and detects threats early, safeguarding long-term value.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in acquisition is a race against time. Ignoring cyber risk can lead to catastrophic breaches, as seen in Marriott, Yahoo, and Change Healthcare. Acquisitions transfer not just assets but technology and risk – every system and vendor can be an entry point if not assessed. Shifting security left through due diligence and adopting a phased, structured approach ensures integration without inheriting hidden threats.