Organizations today are beginning to view the cloud differently. Rather than treat it as a mere infrastructure asset, they now consider cloud as a tool to transform their business. This assumes significance as companies pivot to provide a ‘phygital’ experience to their customers and reinvent multiple processes, thereby creating greater value for all stakeholders.
Industry Cloud – The Next-gen Cloud Revolution
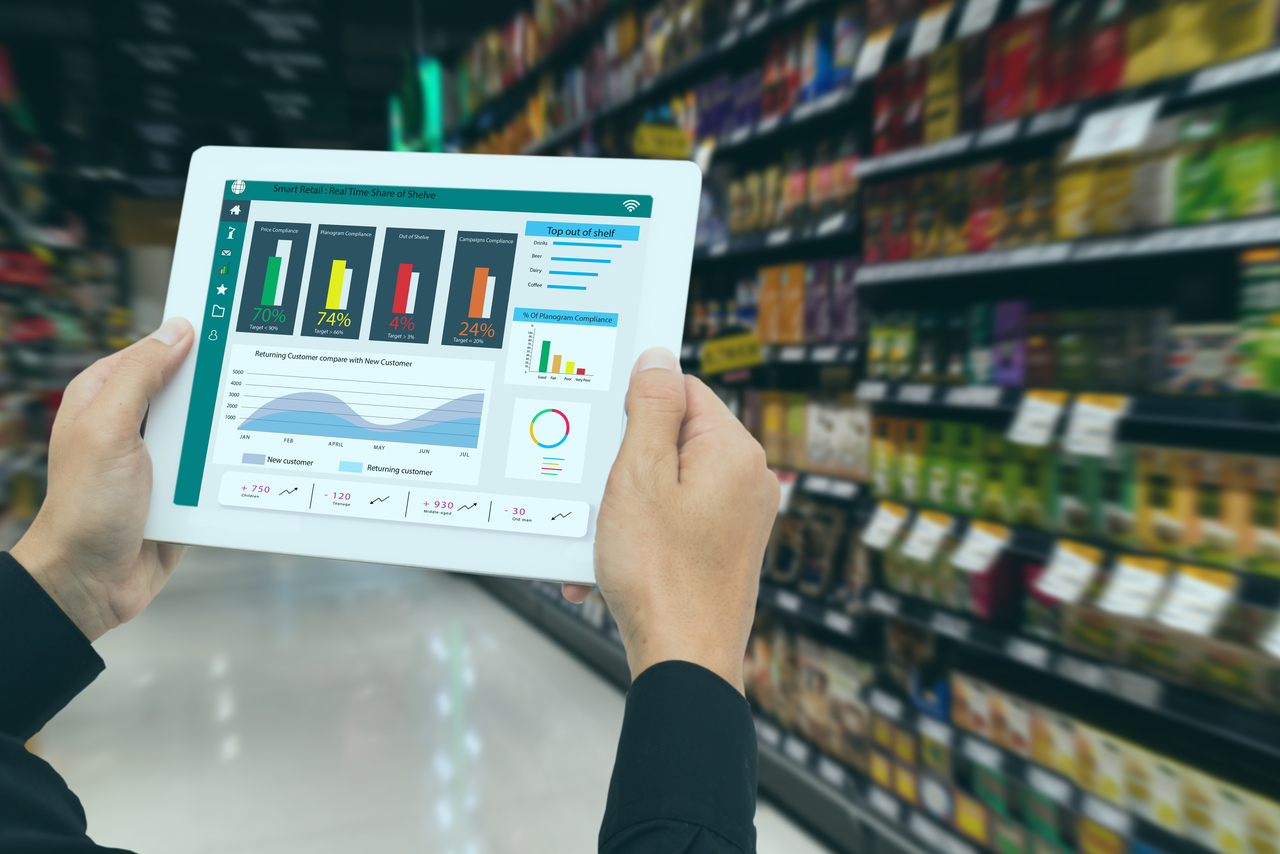
Enterprises are at the cusp of navigating the next-gen ‘cloud revolution’, which focuses on creating custom, domain-specific solutions that enable businesses to offer scale at speed. When modernizing their systems, every industry needs to address specific and unique challenges such as ensuring regulatory compliance and data privacy in financial services, providing simplified and delightful user experience for retail, catering to service personalization in telecommunications, and improving inventory management for manufacturing. This need for industry-specific modernization has paved the way for ‘Industry Cloud’.
An industry cloud focuses on specialized processes with tools and business services dedicated to a specific industry. Designed to mitigate industry challenges, industry clouds accelerate an organization’s go-to-market journey. They are quickly gaining traction as industries prefer solutions that can be consumed as-a-service as well.
Mastering Quality Assurance Practices for Industry Cloud
Adopting an industry cloud presents its own challenges such as:
- Limited customization
- Need for a new user interface and experience
- Security concerns around the end-user data
- Availability of services
- High operational costs
There is a new quality engineering (QE) paradigm that addresses the decoupled nature of industry cloud in an efficient and effective manner.
Its key elements are:
Right-sizing of quality – This approach emphasizes the early involvement of QE in the software lifecycle to develop a robust and optimized master test strategy based on the information available. An assessment-based approach to navigate through business transformation is paramount for ensuring quality.
Thoroughness in coverage – We recommend that enterprises perform parallel testing of all the end-to-end business processes in the current set-up as well as on the industry cloud. The focus is to replicate production-like data and compare the outcomes on the two platforms.
Cost transparency – Businesses are likely to auto scale infrastructure and perform intelligent analysis of service consumption to reduce scale-up and subscription costs. Thus, to drive adoption of the industry cloud, it is important to conduct tests and thereby avoid cost overruns.
Aim for hyper-automation – Adopt an automation-first approach to ensure that QE practices leverage new-age tools across the test lifecycle. Enterprises should assess the technology landscape and discover fit-for-purpose tools that boost efficiency. They should validate infrastructure to ensure resiliency as well as availability and mitigate the vulnerability risks to the setup. They could implement early automation at the microservice/component level as well as robotic process automation (RPA) to test end-to-end business processes. From a testing perspective, the key areas to focus on are:
- UI/UX testing to ensure unified experience across browsers
- Quality checks with huge volumes of data and heterogenous data sources to ensure accurate data workloads
- Penetration testing to detect vulnerabilities and automated testing of IAM
- Static application security testing (SAST) and dynamic application security testing (DAST) to ensure seamless service availability and security
- Performance tests to ensure scalability of the service as well as impact of noisy neighbors and end-user performance tests from across regions to identify impact due to network induced delays
Rise of the Digital Quality Engineering Framework
Market interest in industry cloud is on the rise. Its tailor-fit, innovative, and industry-specific considerations bring significant value such as cost, security, regulatory, and operational advantages with faster time to market. To future-proof the business, quality must be engineered for each industry cloud to ensure that mission-critical applications continue to function with zero defects. The bottom line: a robust quality engineering validation framework is the need of the hour for industry cloud initiatives