Transforming legacy ERP systems to S/4HANA is becoming a strategic necessity for many enterprises in today’s business environment. However, these are extremely complex as they involve either the consolidation of multi-country or multi-business units into a single centralized and harmonized ERP.
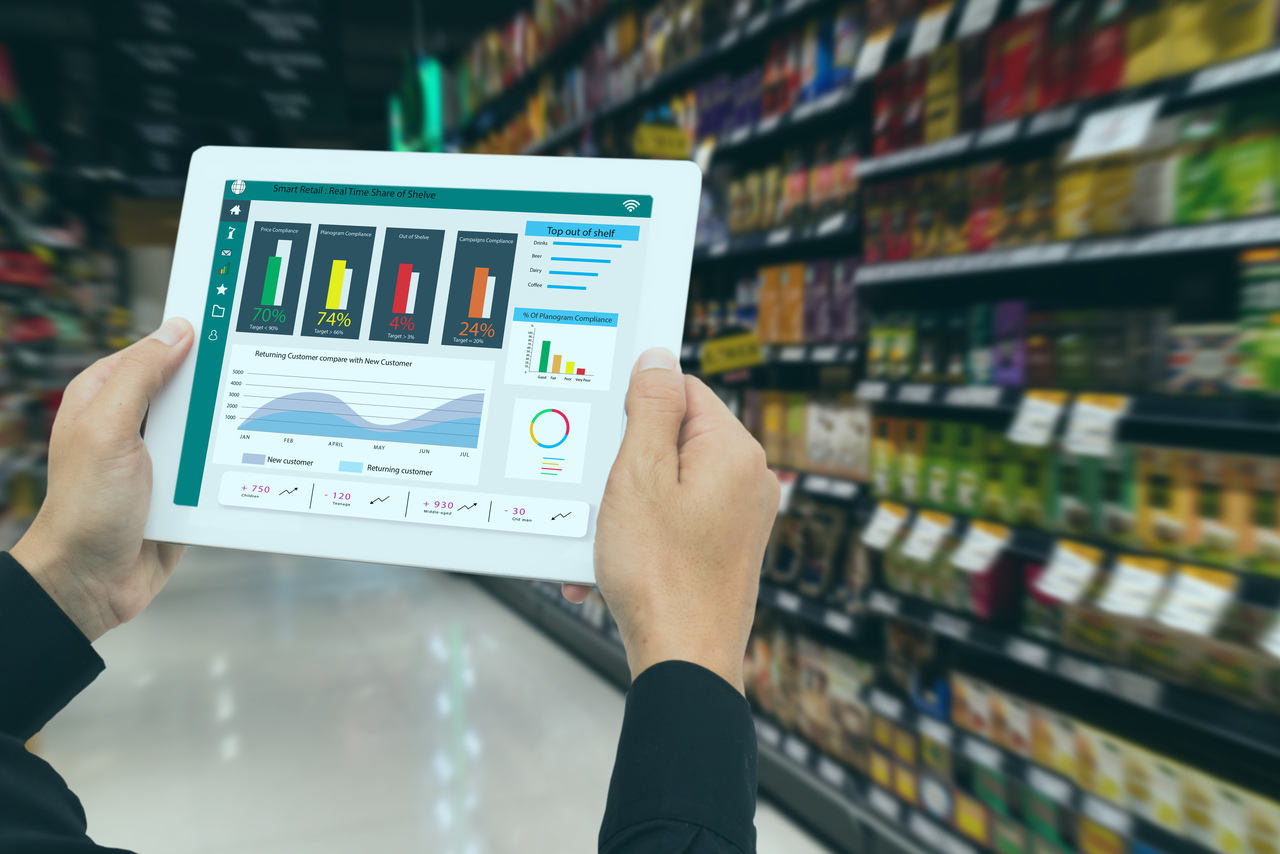
In greenfield transformations, it can often be challenging to calculate aspirational key performance indicators (KPIs) that calculates the degree of operational efficiency and return on investment (RoI) of the transformation. Without a clear approach to tracking KPIs, organizations risk diminished business outcomes.
While any large S/4HANA transformation have Governance boards, they are focused on their specific areas (process, solution, and architecture). However, big picture to maintain alignment and consistency through the various phases of the program needs additional oversight to achieve the committed business KPI.
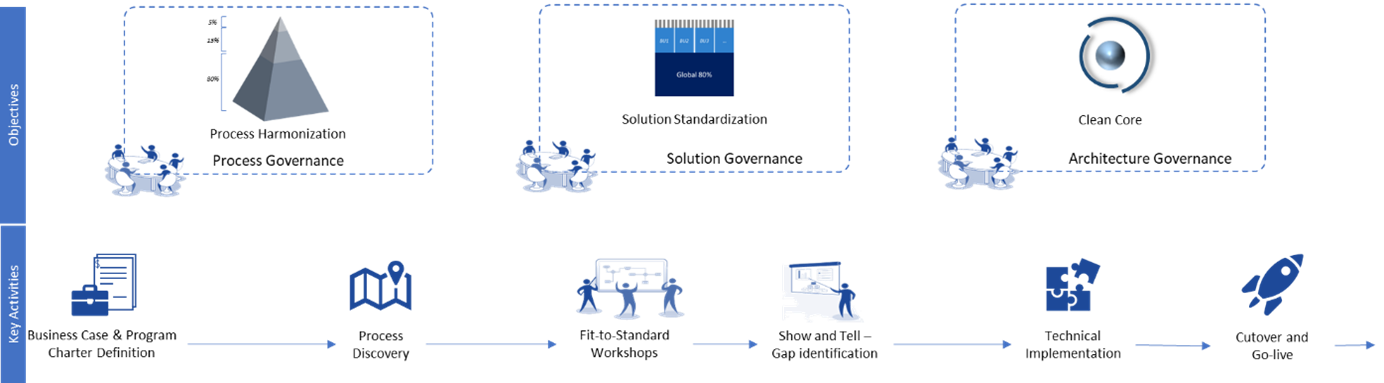
Indicative (not exhaustive) placement of governance boards within S/4HANA transformation
A Game Changing Tool-Based Governance Framework
To address the challenges in KPI measurement and governance, a tool-based framework can be incredibly effective. The Infosys IDEA-Activate methodology offers a comprehensive solution that ties together all governance boards and ensures that KPI measurement is continuous and accurate. Users can build and customize real-time dashboards, help stakeholders monitor progress and make informed decisions. This allows program sponsors and users to take remedial actions, early, based on a holistic view of the implementation process.
Salient features of the Infosys IDEA-Activate Tool-Based methodology is:
· Process Harmonization and Mapping: Once business processes are harmonized and stored in SAP Signavio, they are mapped to SAP business capabilities, helping to identify relevant SAP best practices for implementation.
· Fit-to-Standard Workshops: During the “explore” phase, fit-to-standard workshops use these harmonized processes to create detailed requirements, regardless of the project management tool (e.g., JIRA, Focused Build etc) used, breaking them down into epics and user stories.
· Linking to Implementation: The user stories and tasks are mapped to configuration items or code packages for system implementation. This is used to measure the level of standardization achieved.
· Solution Validation and Governance: The framework can be extended to validate the solution by linking the toolchain with the test suite, ensuring comprehensive process coverage. The architecture governance board uses this data in real-time to oversee and adjust the level of customization as needed.
· Governance and Quality Gates: Quality gates throughout the project phases are documented to ensure thorough governance.
Typically, this tool chain is owned by Enterprise Architect(s), who ensure end-to-end traceability in the BPM tool, and linking development objects to solution gaps, thereby minimizing technical debt and maintaining high level of standardization.
Read this whitepaper on how a tool-based governance framework can help reap greater benefits during S/4HANA transformation programs.