Background
The world we live in today is not built considering the needs of every human being. The products and services we consume are created targeting the mass majority who are abled. But across the world, close to 1.3 billion people are disabled, which means 1 in every 6 people experience some form of disability.
In the WebAIM accessibility evaluation report of the top 1 million home pages published in 2024, 95.9% of the websites had accessibility issues ranging from low color contrast to missing alternative text and many more, making them inaccessible for users with visual impairment. Digital accessibility (a11y) is the inclusive practice of developing digital applications and content accessible to all, irrespective of their abilities.
Countries across the world are prioritizing the accessibility of their digital services for citizens by strengthening the legal framework and associated laws. The baseline for all these laws is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) published by the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) under the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). WCAG is the single shared international standard for digital accessibility which enables all organizations to measure the accessibility of content, sites, and apps for all people, including those with disabilities.
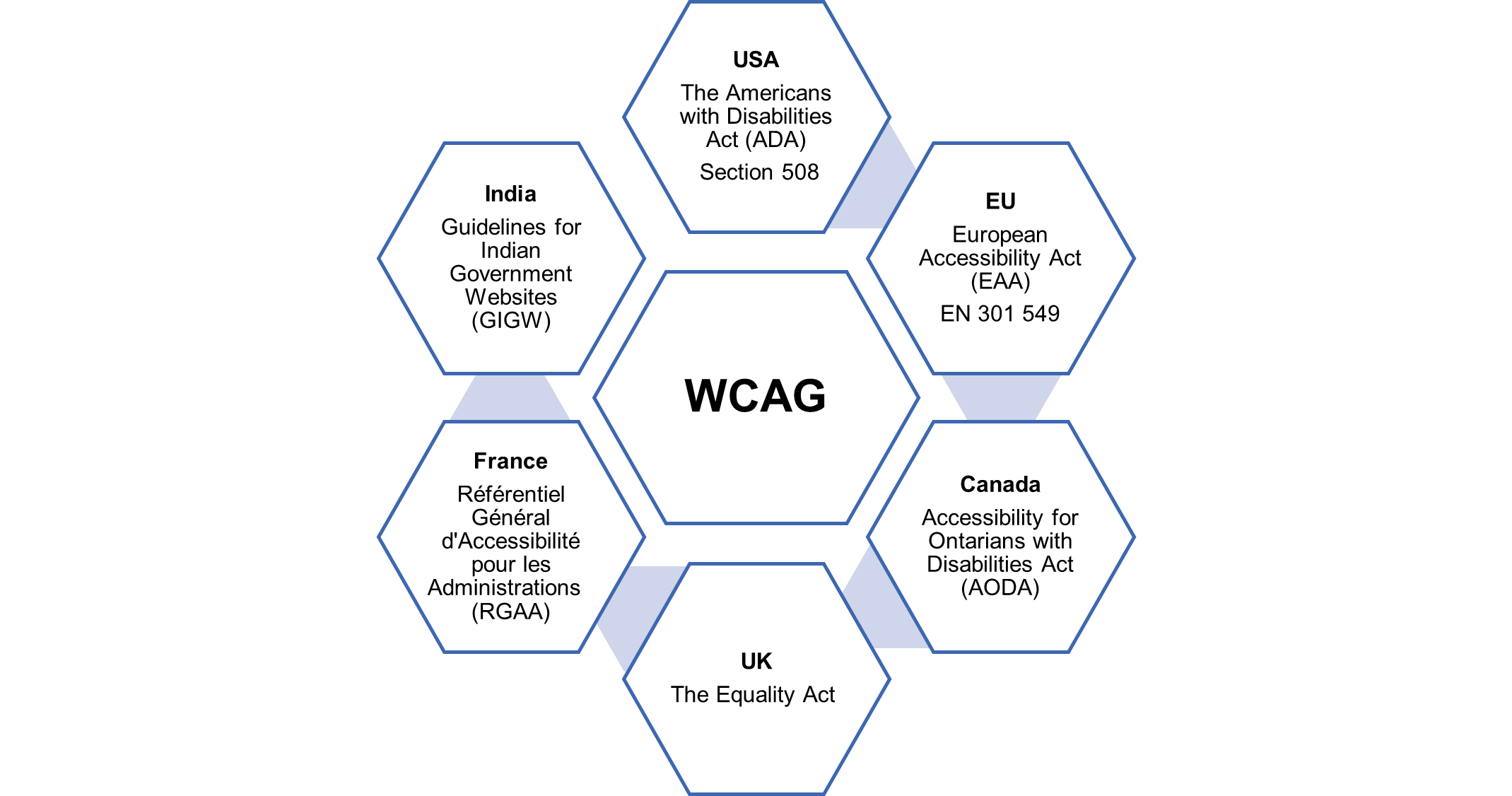
Figure 1 – Accessibility Laws Across the World
The Need for EAA
European Union (EU) has strengthened its commitment to accessibility with the latest landmark law defining common accessibility guidelines for all its member states. European Accessibility Act (EAA) Directive 2019/882 is the European Union (EU) directive that establishes accessibility requirements for ICT products and services. It was enacted on 27th June 2019 and will come into full force on 28 June 2025 for its member states. The directive is applied equally to public and private sector entities. It ensures equal rights and access for all its citizens by removing accessibility barriers and avoiding discrimination. Nonconformance can lead businesses to lawsuits and penalties which are costly and avoidable.
European Union (EU) has understood the power and need of 101 million. As per a 2022 study, this 101 million translates to 1 in 4 adults, or 27 percent of the EU population (older than 16 years) who have some form of disability. Accessibility and Inclusivity practices are a necessity in Europe as disability is on the rise. EU is taking necessary measures to strengthen its accessibility laws for its products and services. The compelling reasons are listed below.
- The EU population is aging, leading to a high number of citizens with disabilities or functional limitations.
- Existing accessibility requirements/laws differ from member state to member state, leading to the fragmentation of a single EU Market.
EAA Scope
The scope of digital products, applications, and services in the purview of EAA includes:
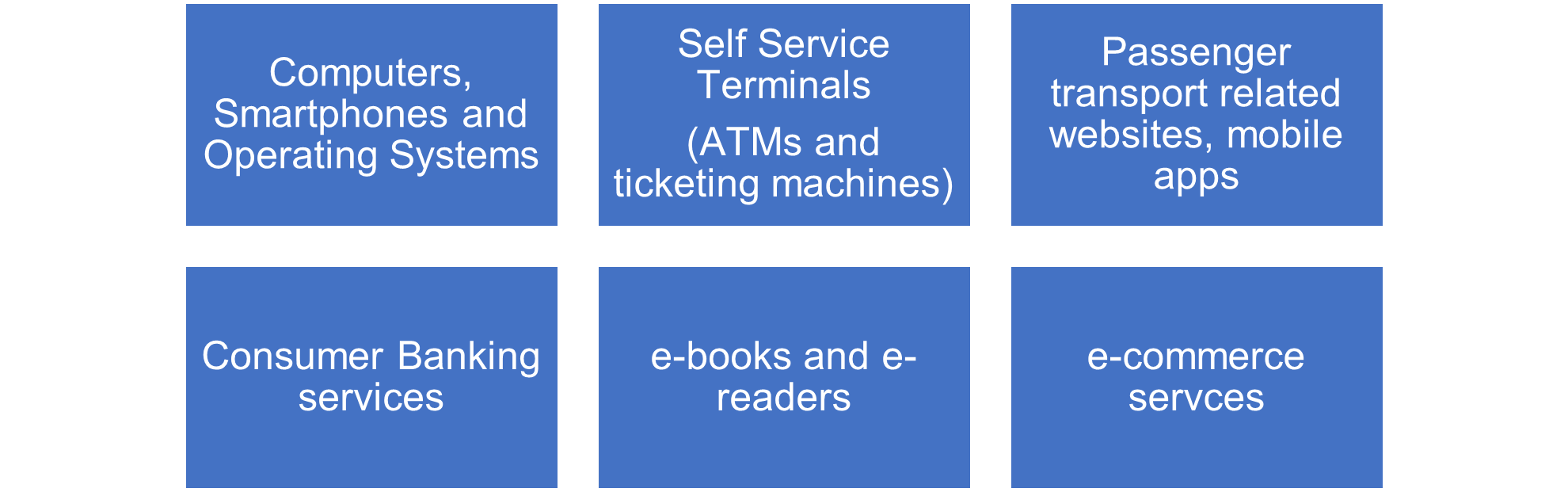
Figure 2 – Products and Services in Scope
Business Impact
To comply with EAA, businesses need to prioritize the accessibility of their products, digital applications, interfaces, and services at the earliest. They need to educate their team on the need for accessibility, scope, and impact of EAA. Businesses should ensure that their digital channels and content are accessible to people with disabilities following the WCAG 2.1 accessibility guidelines. The activities which can be performed on priority are as follows:
- Create of accessibility roadmap for all products and applications of the business landscape.
- Conduct accessibility assessment of existing products and services.
- Perform required remediation activities and code fixes.
- Certify and publish the accessibility compliance.
Benefits
- Improved accessibility across products, applications, services, and content in the EU market benefitting people with disability, the elderly as well as the general public. This increases their opportunities in education, employment, and overall quality of services.
- EAA is equally beneficial for businesses as there is an increasing awareness and demand for accessible products, applications, and services across digital channels. This impacts overall market reach, customer connection and retention.
- EAA noncompliance can lead to lawsuits, fines, and penalties for impacted business players.
References
- Commission, E. (2021). European accessibility act. Retrieved from Employment, Social Affairs & Inclusion: https://ec.europa.eu/social/main.jsp?catId=1202
- Council, E. (2024). Disability in the EU: facts and figures. Retrieved from https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/infographics/disability-eu-facts-figures/
- Directive – 2019/882 – EN – EUR-Lex. (2019). Retrieved from EUR-Lex – Access to European Union Law:https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32019L0882
- W3C-WAI. (2005). WCAG 2 Overview. Retrieved from Web Content – WCAG 2: https://www.w3.org/WAI/standards-guidelines/wcag/
- WebAIM. (2024). The WebAIM Million. Retrieved from WebAIM Projects: https://webaim.org/projects/million/#intro