Introduction
In the spectrum of accessibility, the emphasis has always been on making end-user digital applications and content accessible for all. But what about the developers and computer professionals who are passionate about technology but limited by disabilities in performing their roles to their desired level? Inclusion of people with disability (PwD) in the workplace brings out several benefits of increased diversity, creativity, innovation, and higher financial and shareholder returns for the enterprise. Engineering teams with a diverse focus create inclusive products and services. They think differently resulting in creative solutions that drive innovation. This blog article highlights the challenges faced by PwD developers and the available assistive technologies to overcome the barriers.
Inclusive Development
According to the WHO, 16% of the world’s population lives with some kind of disability of which the majority is not aware or recognized. The disability can be related to visual, auditory, cognitive, neurodiversity, or physical impacting motor movements. The developer challenges encountered are unique to the type of disability and the kind of role they perform in the organization. They use assistive devices and alternate mechanisms for digital access.
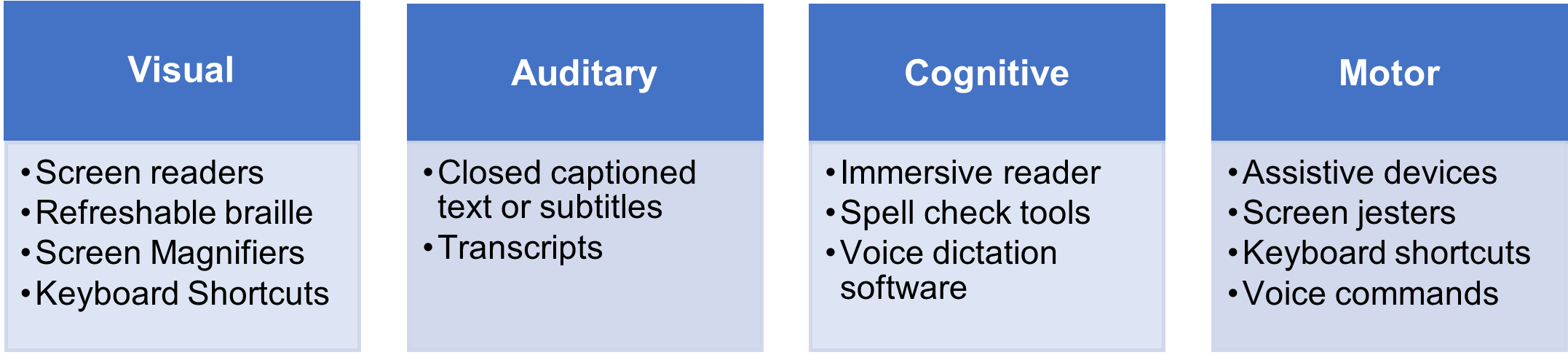
Figure 1 – Methods of Digital Access
PwD engineering team members face several blockers in accessing code via Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), developer tools, debuggers, understanding visual cues, accessing training materials and videos, and actively participating in team meetings and training sessions. People with cognitive or neurodiversity encounter challenges in analyzing and creating complex code libraries, resulting in increased cognitive loads. People with motor disabilities are unable to use mouse and keyboards and face strain injuries from repeated use.
By embracing the power of modern technology supported by accessible tools, and assistive mechanisms following a multi-sensory approach, PwD developers can be empowered to perform their tasks seamlessly and efficiently with improved productivity leading to the creation of inclusive teams within every global enterprise. Built-in accessibility features should be available in all IDEs and developer tools to access application code, databases, and functionalities via screen readers and assistive technologies. Supporting information like API documentation, online developer forums, and blogs should be accessible and inclusive.
Modern-day IDEs like Visual Studio include in-built accessibility features to adjust zoom levels, select high-contrast themes, and enable keyboard and tab navigation. IDEs support screen readers and keyboard-only access. They have built-in audio cues and keyboard shortcuts for easy navigation and debugging. Visual Studio has recently included an AI-powered IntelliCode utility with an in-context auto-completion feature and the capability to do repeated edits using quick actions. Immersive readers enable easy access to project documentation and training documents. AI-based Microsoft365 Copilot has rich accessibility features. MS team offers speech-to-text conversion and text-to-speech conversion capabilities employing Azure cognitive services.
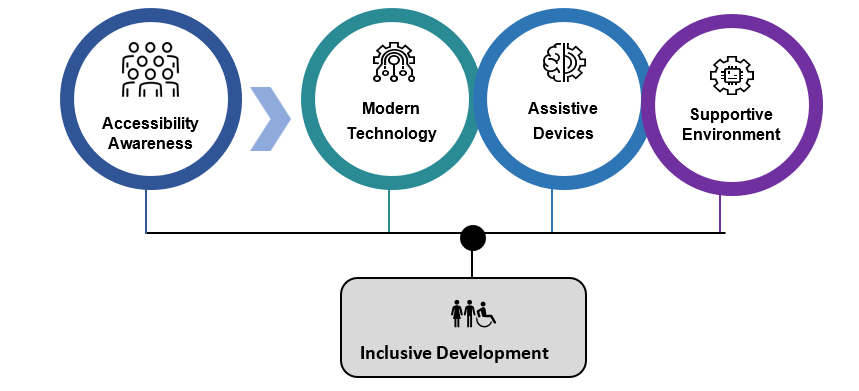
Figure 2 – Inclusive Development
Inclusive development brings numerous benefits to the developers, project teams, the enterprise, and the community. Accessibility improves the efficiency of PwD developers. Tasks performed taking hours can be completed in minutes with the use of assistive technology resulting in increased productivity with improved overall confidence. Improved participation of PwD developers creates an inclusive and diverse workforce with enhanced creativity and innovation. An inclusive team creates inclusive products.
Conclusion
Enterprises should focus on bringing awareness, a supportive environment, assistive tools, and modern technology to embrace inclusive development. Multi-sensory approach integrated with in-context AI capabilities can support PwD developers to achieve more and gain team trust, limiting overuse and fatigue. Inclusive development is indeed a great step forward in increasing the participation of PwD talents in the workforce and becoming an equal employment opportunity provider bridging the great digital divide.
References
1. Accenture. (2018). Getting to Equal: The Disability Inclusion Advantage. Retrieved from Accenture.com: https://www.accenture.com/content/dam/accenture/final/a-com-migration/pdf/pdf-89/accenture-disability-inclusion-research-report.pdf#zoom=50
2. Microsoft. (2023). Inclusive Development: Empower Every Developer and Their Teams to Achieve More | Ability Summit 2023. Retrieved from Ability Summit: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yNaXrk6i04c
3. WHO. (2023, March 7). World Health Organization – Fact Sheets – Disability. Retrieved from World Health Organization: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/disability-and-health