Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) is a lifeline for Manufacturers and creates a monolithic ecosystem for the entire factory operations – interfacing OT and IT systems and bridging the information from the Factory to the enterprise. As Manufacturers expand their footprints with new product introductions (NPIs), add new sites / factories, acquire similar factories, and seek a wider presence into the global markets, the key challenges faced by these Manufacturers is to streamline their operations and put up an optimized and standardized Production process framework across the terrains. Most of the Manufacturers choose for “Horses for Courses” approach and end up with a bunch of MES platforms / technologies / applications driven by site sentiments.
MES application for a site / factory is defined to be a ‘unique’ instance by the ultimate consumer of the application as he tends to live by the application. These emotions eventually call for a bespoke solution; tailored to the specifics of their processes and day-to-day functions. With multiple site deployments, the Enterprise IT usually aims to design and develop a global golden copy solution that can be replicated across all the sites, adhering to best practices. However, the site business / Site crew has their own ways and vision.
Based on various combinations and industrial deployments, we have experienced the following categories of MES templatization approaches in the industrial space: –
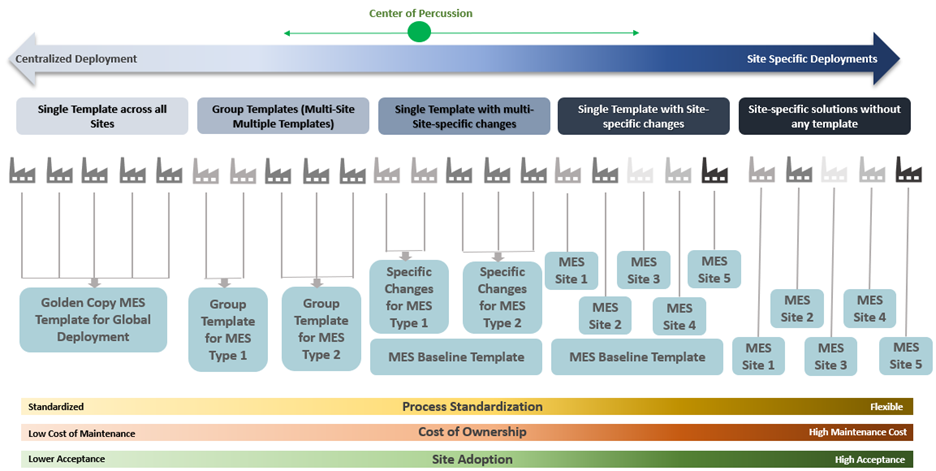
Figure 1 – Options for Templatizing MES Applications in Industrial Space
A hybrid option, more towards the center of the frame above seems to be the go-to option for most of the Manufacturers that provides a sense of stability. I have tried to build a comparison between these options based on the industrial usage: –
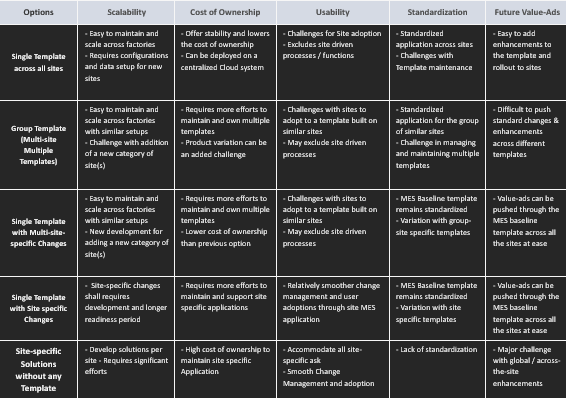
While Manufacturers check for their budgets and spend on Manufacturing execution processes and technologies, it is imminent that MES has been the key application and a blend of MES with IIOT can help Manufacturers to improve the overall OEE and, hence accelerating productivity. The key factors that can influence their decisions on the approach to templatization (from the options listed above) are covered below –
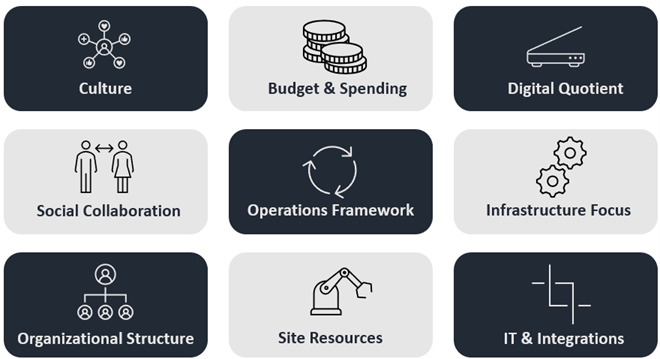
Figure 2: Key Factors influencing the Approach to MES Templatization
Manufacturers can choose to leverage an off-the-selves packaged application offered by various vendors or can tailor their own customized MES platform. In either case, specific strategies are adopted in terms of templatization by industries and the decisions are a factor of usage, complexity, and coverage. The chart shows the templatization categories by industries and provides a fair idea on how the industries have worked on setting up their Manufacturing Execution ecosystems (applicable in case of Multiple sites).
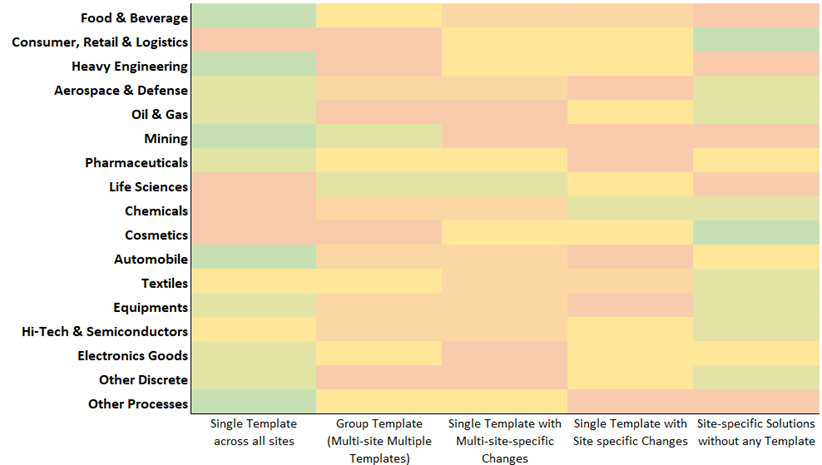
Figure 3: How the industry has applied the various Templatization options for MES systems
Based on various factors and industrial study, Templatization of MES application has been a challenge all the times. The enterprise must seek support and acceptance from the site business and IT team to choose for the specific option for templatizing the MES application. Change Management and site adoption are key to the success of MES rollouts and hence the decision on the options for MES templates must ensure alignment with the site personnel / group.











Nice extensive blog Amit!