In today’s fast-moving supply chains, efficient distribution is critical to business success. Supply chain managers play a key role in leveraging Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) to manage orders, inventory, purchasing, and logistics, which can make them feel valued and essential to operational success. However, traditional rule-based processes often struggle with changing demand and complex operations.
AI enhances Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) by adding predictive intelligence to existing workflows. Instead of reacting to issues after they occur, organizations can anticipate demand, optimize inventory, and automate key decisions. This results in fewer stockouts, lower excess inventory, faster order fulfillment, reduced logistics costs, and a better overall customer experience.
Why Distribution Efficiency Matters and Challenges in Oracle EBS
In today’s customer-driven marketplace, distribution efficiency is vital for revenue, margins, and customer loyalty. Recognizing this importance can motivate stakeholders to prioritize speed, accuracy, and cost control, which define success. Even minor delays or inventory misallocations can lead to lost sales, higher freight costs, dissatisfied customers, and margin erosion.
Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) serves as a robust transactional system of record across Order Management (OM), Inventory (INV), Warehouse Management (WMS), Purchasing, Logistics, and optionally Oracle Transportation Management (OTM). It ensures reliable execution, control, and auditability of orders and inventory movements. However, distribution environments are becoming increasingly complex due to:
- Rapidly fluctuating demand and promotions
- Shorter product life cycles and frequent product introductions
- Global, multi-warehouse, and multi-supplier networks
- Higher expectations for fast, accurate deliveries
- Tighter service level and cost-to-serve constraints
Despite EBS automation, many planning and execution decisions still rely on manual analysis and static rules. AI can provide predictive insights for inventory replenishment, order prioritization, warehouse labor planning, and delivery scheduling, reducing stock-outs, excess inventory, and logistics costs. This makes distribution more proactive and efficient.
AI enhances Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) with predictive and optimization capabilities. Instead of replacing EBS, AI adds an intelligent layer that empowers decision-makers with proactive planning, automated decision-making, and end-to-end visibility, transforming distribution from reactive to predictive performance and fostering confidence in future operations.
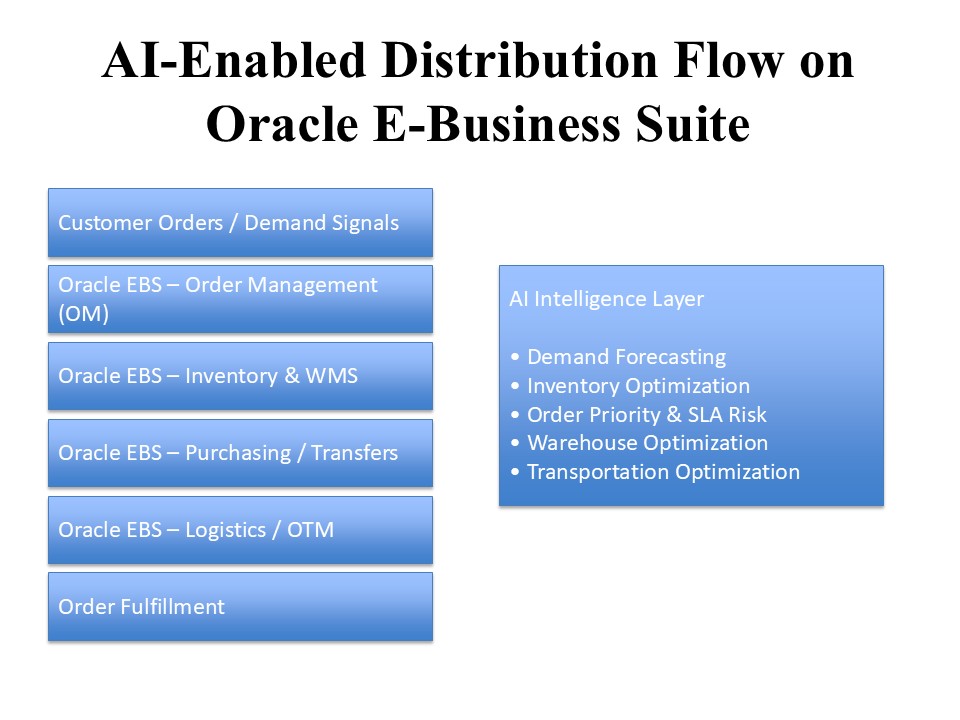
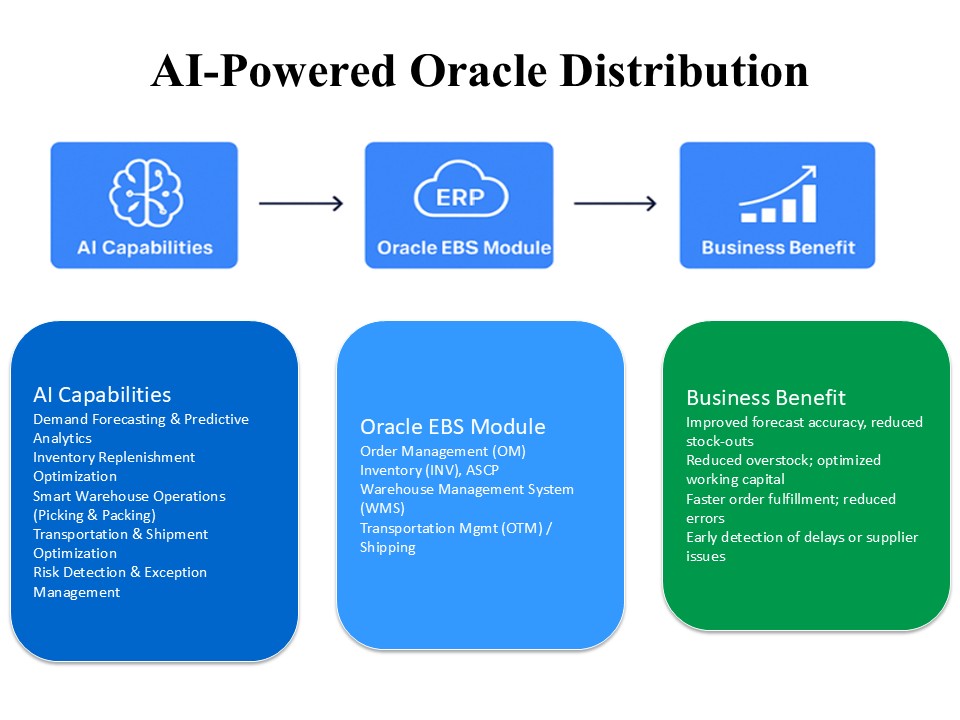
Figure 1: AI-Enabled Distribution Flow on Oracle E-Business Suite
Figure 1 illustrates how Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) continues to function as the transactional execution layer, while AI operates as an intelligence layer that continuously analyzes operational data, predicts risks, and feeds optimized recommendations back into EBS. This closed-loop flow enables proactive, data-driven distribution execution without compromising system control or auditability.
Traditional vs. AI-Enabled Distribution
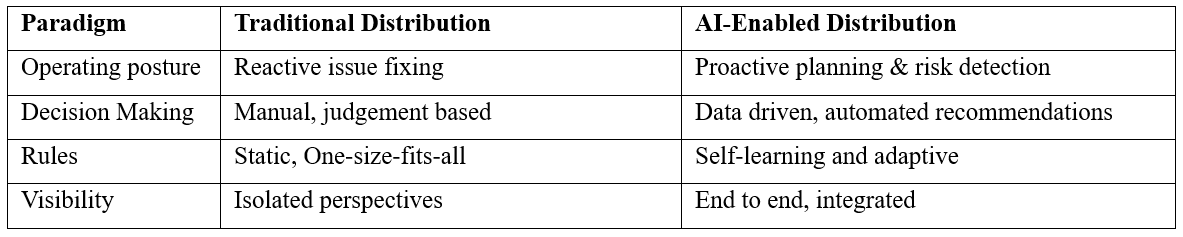
As distribution complexity grows, AI-enabled execution is becoming essential for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and delivering consistent customer service within Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS)-driven supply chains.
AI in Supply Chain & Distribution – Enhancing Decision-Making and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) adds an intelligent decision layer on top of Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS), empowering supply chain and distribution teams to make smarter choices and feel more confident in their operations. By continuously learning from transactional data, master data, operational events, and external signals, AI helps organizations analyze trends, predict future outcomes, and recommend optimal operational actions. Unlike traditional systems that rely heavily on manual interpretation, AI makes distribution operations more responsive, efficient, and resilient.
As illustrated in Figure 1 (AI-Enabled Distribution Flow on Oracle EBS), Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) continues to function as the system of record for execution. Simultaneously, AI serves as an intelligence layer that analyzes data, generates insights, and provides recommendations to EBS for controlled execution, minimizing disruption to existing workflows and user roles.
Within Oracle-based supply chain environments, AI enhances distribution performance across three core dimensions, including metrics like order accuracy, lead times, and inventory turnover, providing measurable improvements that support strategic decision-making.
A. Better Visibility and Insight
Many distribution challenges originate from limited visibility into real-time supply, demand, and operational constraints. While Oracle EBS holds rich transactional data across Order Management (OM), Inventory (INV), Warehouse Management (WMS), Purchasing, and Oracle Transportation Management (OTM), critical patterns are not always apparent in standard reports.
AI improves visibility by:
- Aggregating and harmonizing data across multiple EBS modules
- Surfacing non-obvious patterns, correlations, and trends
- Identifying exceptions and risks early, along with contextual insights and recommended actions
Outcome: Raw transactional data is transformed into actionable intelligence that supports faster and better-informed decisions.
B. Predictive Decision-Making
AI models leverage historical transactions, demand variability, lead times, supplier performance, seasonality, promotions, and operational trends to forecast and predict likely outcomes, including:
- Near-term demand (3–12 weeks) by SKU and location
- Imminent stock-out or excess inventory risks
- Potential shipment delays and service-level failures
By shifting from hindsight-based reporting to forward-looking insights, planners can anticipate disruptions and proactively mitigate risks rather than react after issues occur.
Outcome: Distribution teams prevent problems instead of firefighting them.
C. Intelligent Process Automation
AI operationalizes insights by recommending or in some cases automatically executing—optimal actions within time-sensitive distribution workflows. Key examples include:
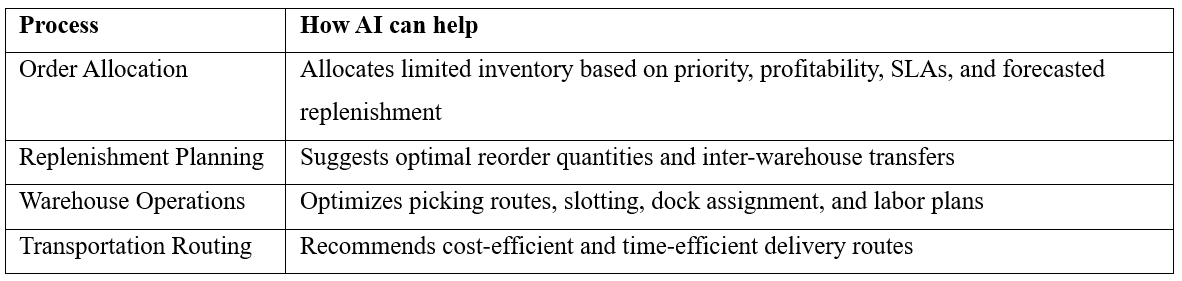
Outcome: Faster, consistent decisions aligned with business objectives.
Instead of relying on human judgment alone, the system recommends or executes the best action based on real-time data.
How AI complements Oracle EBS
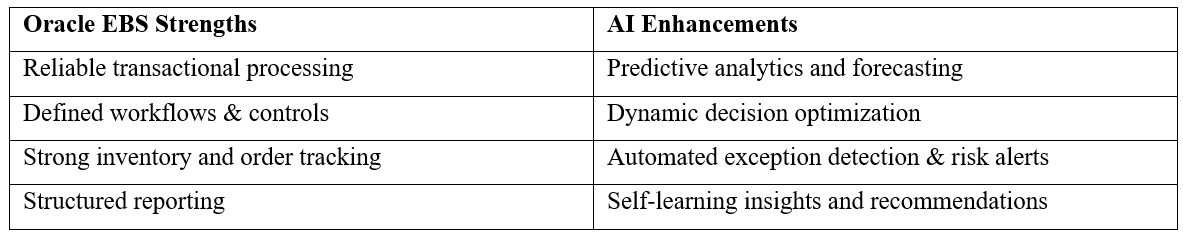
In summary, AI does not replace Oracle EBS. Instead, it acts as an intelligent engine that augments existing systems, helping planners, warehouse managers, and logistics teams plan better, respond faster, and operate more efficiently. Supporting scalable, efficient, and controlled supply chain operations reassures teams that they can confidently manage growth and complexity, ensuring stability and reliability in their workflows.
Key AI Applications in Oracle EBS Distribution
AI enhances Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) distribution operations by embedding intelligence at every step of the distribution lifecycle, helping stakeholders feel more confident in their decision-making. Rather than relying on manual decision-making or static configuration rules, AI continuously analyzes operational data and applies real-time intelligence to optimize inventory planning, order prioritization, warehouse execution, transportation, and risk management.
As shown in the AI-enabled Oracle distribution flow, Oracle EBS continues to execute transactions across core modules. At the same time, AI operates as a decision layer that predicts outcomes, recommends actions, and feeds optimized decisions back into EBS for controlled execution, fostering trust in the system’s reliability.
The following sections outline key AI applications that enhance Oracle EBS modules, including Order Management (OM), Inventory (INV), Warehouse Management (WMS), Shipping, Oracle Transportation Management (OTM), and Advanced Supply Chain Planning (ASCP). These innovations aim to support your strategic objectives and improve operational efficiency.
A. Demand-Aware Allocation and Order Prioritization
When demand exceeds available inventory, determining which orders to fulfill first becomes critical. Traditionally, this has relied on static rules, such as FIFO, or on manual judgment.
What AI does:
AI replaces static prioritization with dynamic allocation by considering customer value, contractual SLAs, forecasted demand, and incoming replenishments. To achieve this, organizations need to ensure accurate, real-time data collection and integration across multiple sources, which may require infrastructure assessments and improvements in data quality.
Impact:
- High-value and strategic customers are served first
- Fewer order cancellations, escalations, and service failures
- Better alignment with profitability and service objectives
EBS Modules Impacted: Order Management, Inventory, ASCP
B. Predictive Inventory Replenishment
Traditional replenishment approaches often use fixed reorder points that fail to adapt to real-world demand and supply variability.
What AI does:
AI dynamically adjusts reorder points and safety stock levels by forecasting demand at the SKU-location level and analyzing seasonality, consumption trends, supplier reliability, and variable lead times. Organizations should plan phased implementations, starting with pilot projects, to evaluate benefits and address integration challenges over a typical timeline of [X] to [Y] months.
Impact:
- Fewer stock-outs for high-velocity items
- Reduced excess and slow-moving inventory
- Improved working capital utilization
EBS Modules Impacted: Inventory, Purchasing, ASCP
C. Smart Warehouse Operations
Warehouse performance directly affects fulfillment speed, accuracy, and cost.
What AI does:
AI optimizes warehouse execution by improving slotting strategies, pick paths, wave planning, dock scheduling, and labor planning based on workload forecasts and operational constraints.
Impact:
- Faster picking, staging, and loading
- Higher productivity per warehouse resource
- Reduced fulfillment time and handling errors
EBS Modules Impacted: WMS, Inventory, Shipping
D. Transportation Optimization
Transportation involves balancing cost, service, and capacity while managing uncertainty.
What AI does:
AI recommends cost- and time-optimal routes, dynamically assigns carriers, and predicts transit risks based on traffic, weather, and historical carrier performance.
Impact:
- Lower freight and transportation costs
- Improved on-time delivery performance
- Reduced manual transportation planning effort
EBS Modules Impacted: Shipping, Oracle Transportation Management (OTM)
E. Risk Detection and Exception Management
Operational disruptions such as supplier delays, demand spikes, warehouse congestion, or forecast errors often surface too late.
What AI does:
AI continuously monitors operational patterns, detects anomalies early, and triggers alerts with guided corrective actions.
Impact:
- Fewer emergencies and reactive firefighting
- Faster containment and recovery from disruptions
- More stable and predictable distribution execution
EBS Modules Impacted: Order Management, Inventory, WMS, ASCP
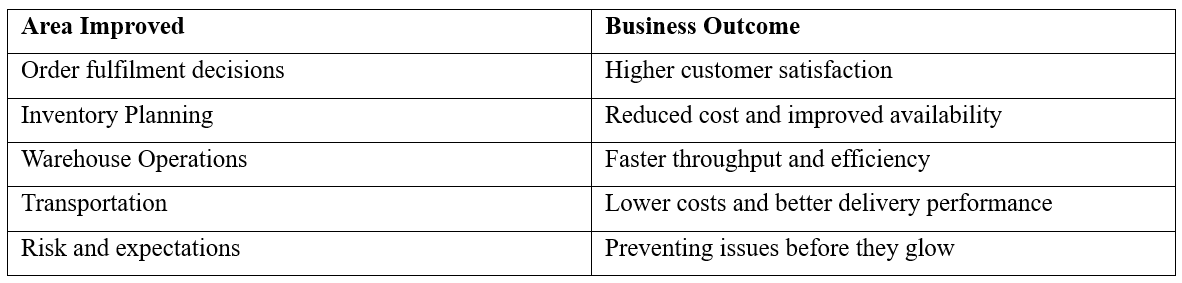
As a summary, AI enhances Oracle EBS distribution not by changing core process, but by making them smarter, faster, and more adaptive. It provides real-time intelligence that supports smarter decisions in:
Integration Considerations – Data Quality, AI Engines, and Organizational Change
Adopting AI in an Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) distribution landscape is a business transformation initiative not merely a technical add-on. While AI can significantly enhance planning and execution, its success depends on data readiness, seamless technical integration, and effective change management across the organization.
To realize sustained value from AI-enabled distribution, organizations should focus on the following strategic pillars.