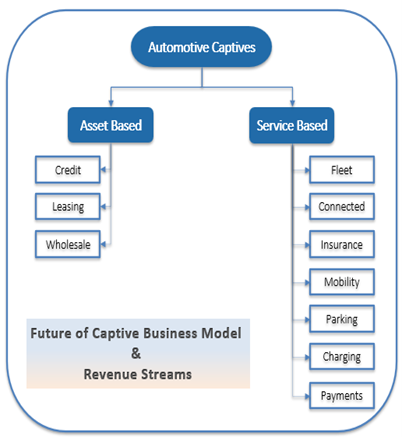
The automotive Finance business model (both captive & non-captive) is going through a much-needed transition phase triggered by the new age customer demands. The traditional model is unable to meet the growing customer demand for flexible and usage-based mobility solutions. The ongoing model, which is mostly confined to OEMs, now demands a bimodal to broaden the offering based on customer needs- Covering the Full-service vehicle leasing, fleet management and new mobility solutions.
The future of automotive banking sector looks promising and is expected to recover from the pandemic-induced drop in leasing & Fleet. From Bank’s Perspective – The low-interest environment along with the economic circumstances affected their prime revenue generation stream of net interest margins and forced them explore and diversify various fee income sources to sustain profitability. Automotive Banking is one such source, where banks are focusing to excel. According to Allied Market Research, the industry is forecast to record a compound annual growth rate of 11.5% and will surpass $5.62 billion by 2031, up from $1.92 billion in 2021.
Providing wide range of offerings in line with the new age customer expectation – fast, easy-to-pay, personalized services, will drive the growth and revenue opportunity from this sector. Globally, large banks started betting on Fleet leasing as a potential growth area considering margin pressure faced by the core retail banking operations. Market is witnessing the trend of large banks either fully or partially owning the fleet management companies who provide complete Vehicle Mobility Solution. Bank’s ability to embed the right financial offerings with the non-financial products, services, or solutions at the right point is the key strategy going ahead.
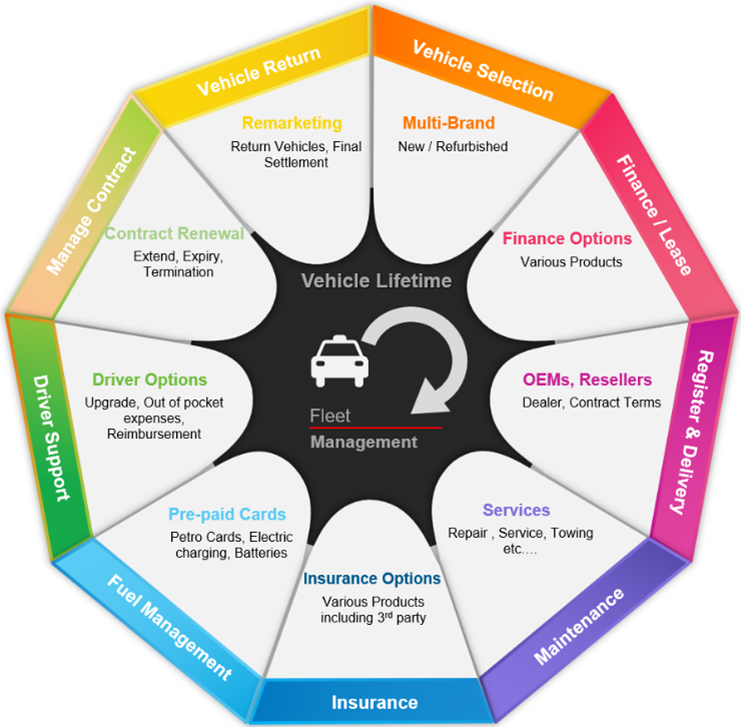
A Snapshot on Vehicle Mobility Solution: Managing Revenue from Leasing, Rental and Fleet services.
The word ‘Leasing’ in vehicle mobility world means arranging the finance for purchasing the vehicle and providing the services for the purchased vehicle and ‘Fleet’ means ‘Leasing’ without financing.
The Mobility Solution can be broadly classified into four categories:
- Operational Leasing, handling end-to-end vehicle fleets life – from Vehicle Purchase till its resale.
- Fleet management for all services, Provisioning of services outside the vehicle purchase
- Fuel card Management
- Technology Services – Connected Car
Customers who need vehicle leasing and mobility solutions will range from large corporates to small and medium companies and even individual retail clients. Business Organization realizes that managing and implementing the fleet policy is not their core activity rather it should be managed outside the core business operations with a proper monitoring and control. The servitization trend in the market has brought in expert service providers in fleet management too. Specialized vehicle mobility solution providers are available with whom organizations can move away from their in-house fleet management. Organizations can get in touch with the full-service solution provider and give their requirements. Based on the customer requirements, Solution provider work on a deal and create a customer quote out of it considering various factors like credit risk limit etc… Once the quote is agreed and signed, the solution provider starts processing the customer request.
For vehicle lease service, the rate / price gets fixed based on multiple factors like – type of the vehicle, the planned usage duration, planned mileage use, resale value etc. The charges are then invoiced and collected from the customer based on the periodic bill cycle basis, as agreed in the contract.
For providing an end-to-end mobility solution, the provider should also have to deal with related support services, Value added services along with the core leasing service. In a complete mobility eco system, the solution provider must deal with multiple entities – OEMs, Suppliers, Dealers, Drivers, Fuel companies, Insurance Companies, Fleet, Taxi/ Cab Services, Tyre dealers, accessory providers, Tech players etc. Customers can opt for wide range of services, for which they will get a single invoice from the Solution provider no matter the service is done by 3rd parties.
The total solution provider will manage individual players and will get it settled separately. For example, the vehicle is to be leased, based on the availability, a purchase order is placed with the OEMs, Suppliers who provide services like tyres, towing, etc. they will get payment from the Solution provider. For such services, Solution provider receives an invoice from the supplier. The solution provider is also eligible for commissions from some of the suppliers in the value chain, for example, Insurance Companies to pay a commission amount for the product they sold to end customers via the solution provider.
There can be specific cases for example in the case of Fuel cards, where some Fuel station networks are unable to send out a legal invoice to the mobility Solution provider, instead they would be sending a transaction file containing the consumption details of the services given to the customers. As per the agreement between Fuel networks and the solution provider, the later must generate the invoice based on behalf of the Fuel network.
Hindrances in Revenue Management faced by Automotive banking Business.
Due to the complex nature of the automotive industry and huge financial transactions involved in this business, there are a lot of challenges to deal with.
- Managing multi-entities for a Transaction: Processing of same transaction with multiple billable entities based on varying transaction context.
- Complex Pricing Structures: Dynamics in customer options, packages and supplementary services and Seasonal pricing and warranty-based pricing.
- Contrasting Billing Cycles: Different components may have different billing cycles or billing terms.
- Currency & Interest Rate fluctuations: Handling currency conversion and multi-currency support, Managing varying loans or leases rates with added variation factors like credit score and market conditions.
- Proving and managing customer Flexibility – Different usage patterns, maintenance needs, multi-channel transactions, electronic invoicing
- Dispute Management: Customers can dispute bills in full or partial charges in case of any billing discrepancies, warranty claims, or service charges. Resolving these disputes efficiently to the satisfaction of the customer is essential for maintaining a positive reputation.
- Legacy Systems, Integrations & Cross-platform compatibility: Handling modern billing challenges like personalized billing. Integrate the billing systems with various banking systems and partner systems.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to various regulatory amendments which includes taxation, consumer protection, and financial reporting.
Multiple Billable entities involved in Mobility Solutions.
Revenue management In the Leasing and Fleet Management business, the Solution Provider deals with various entities like customer, suppliers/third party vendors/sub-contractors, brokers, intra company offices and drivers. These entities are associated with the same or multiple transactions and are either billed by the Solution Provider or they bill the Solution Provider for the services.
Customer:
A customer is someone who makes use of the services (either lease or purchase of vehicle, as maintenance or assistance) of Solution Provider. They could be an individual, small, or big corporate for which they are invoiced by the Solution Provider.
Suppliers:
Suppliers are the real actors in providing a service to the end customer, even though the Solution Provider is dealing with the customer and charging for the same. It could also be possible that these suppliers are normal customer of the Solution Provider for which the dealings for each of the roles (customer & supplier) are separated out.
Brokers:
Brokers are company or individuals who bring business (customers) to the Solution Provider. For every deal that the broker gets in for the Solution Provider, a certain commission is given.
Intra Company:
Intra Company refers to the group concerns of the Solution Provider working in various geographies/countries. Even though these companies come under one group, for any business dealings within these companies, invoices are raised against the servicing company.
End Users / Drivers:
For all agreement with the customer, it is mandatory to collect the driver information. This is captured not only for information purpose, but there are cases where some components of the invoice need to be raised against the driver than the actual customer as part of the contract.
This will be for instances where the contract is made between the customer (enterprises) and the Solution Provider for providing the vehicle to its employee use. Employees (drivers) could upgrade the vehicle (different from what the employee is eligible for) by paying the difference for this upgrade. In this case, the contract would be the same, but two invoices are to be raised – one for the company (regular contract) and one for the driver for the differential charges.
Sometimes a driver/end user can be a supplier (Scenario: While Driving the Car, it is found that the head light bulb got fused and driver changes the bulb from a shop. In this case, the driver pays the bill and the Solution Provider must pay back the driver or his company).
White Brands:
These are companies who own the end customer but uses the Solution Provider’s eco system for providing the services. From a client relationship point of view, the core Solution Provider is unknown as the client has signed the contract with the white brands. Here the Solution Provider, Invoices the white brands for the services (it can also be an event-based charging).
Mobility Solution Contract – How it gets orchestrated?
A contract is an agreement that contains the conditions for offering the service to the customer. Contracts can be of rental, maintenance contracts. A service contract contains validity dates, cancellation conditions, price agreements (Pricelists), and information on possible follow-up actions.

Product & Service Catalogue
The new model open opportunities for captives to finance, operate and maintain fleets. Hence captives need to deliver broader range of products and services.
Subscription models and usage-based models will be the core revenue generation strategies for the business to offer flexible and personalized deals to the customers. The IT system and processes to support and adapt the these strategies will be the key to be success among competition.
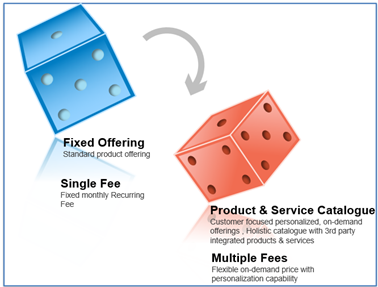
Product and Service
Typical fleet management products and service offerings cover the entire vehicle lifetime. The total cost of ownership (TCO) for the customer is the key factor while designing products, services and packages in order to identify cost saving potential and reducing operating expenses. Mobility Solution providers follow innovative product strategies including customer specific product bundling, Subscription based, pay per usage strategies to reduce the costs for their customers.

Product
A product is an association of one or several services. A Product must have a price by itself or build from the addition of the prices of its associated services.
Service
A service is the result of one or several processes combined with options. It has a commercial value, and CAN NOT be individually sold without being associated to a Product (one service product). Options do not affect the OUTPUT process but may change the cost/value of the service delivered.
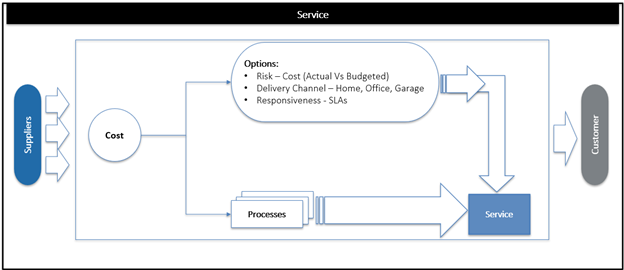
Options
An option is a variation of a service. There can be two categories of options. (1) Transversal and (2) Specific.
- Transversal options:
The transversal options are options that can be associated to any services. They are.
Risk (actual Cost, Budgeted…)
Delivery channel (at home, garage…)
Responsiveness (24hrs, week …)
Billing (standard, on a usage basis…)
- Specific options:
A specific option can be defined as an option necessary to a specific service and has no significance outside this service domain (no point in making it a transversal option).
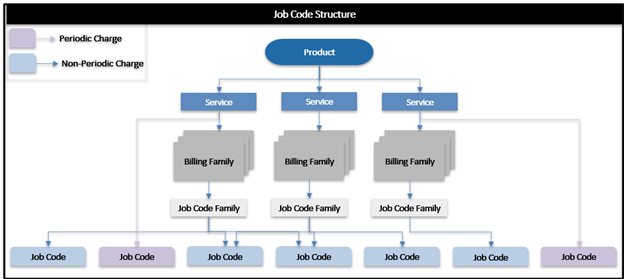
The Catalogue Structure – Product, Service and Job Code
Job code is the lowest level entity in the product structure, against which rates are defined and bill lines are created. Job codes can be of two types – (a) Periodic and (b) non-Periodic.
Periodic charges are defined at the service level whereas non-Periodic charges are at the job level. A collection of job codes forms a Job code family and will always be part of a billing family. It is possible to have the same job code belonging to multiple job code families in the whole structure. For example, the job code ‘Towing’ can belong to two different job code families – ‘Maintenance’ and ‘Assistance’.
Package:
The package is a marketing, commercial view of a bundle of Products that can sell to end customers. A Package will be identified by a unique name and the name must be consistent across geographies. The creation of the Packages is a marketing process. The quote out of a deal workflow will have only one package. The products included in a package can be mandatory or optional. The package concept is useful to sell a group of products especially for SME’s (where the choice will be very limited). Large accounts will have more open packages where products can be chosen.
Transactions for Bill Generation – A Synopsis
Post the lease or purchase of a vehicle, the mobility solution provider has to manage the subsequent transactions and have to manage the monetization part. There can be mainly four contexts where customers seek services – Assistance, Maintenance, Accident and Contract. In each such context, there will be a triggering action followed by its related Service event and finally the actual action or job to be completed to fulfill the request. The context and events can be part of a package or product. All contexts and events can also have standalone existence.
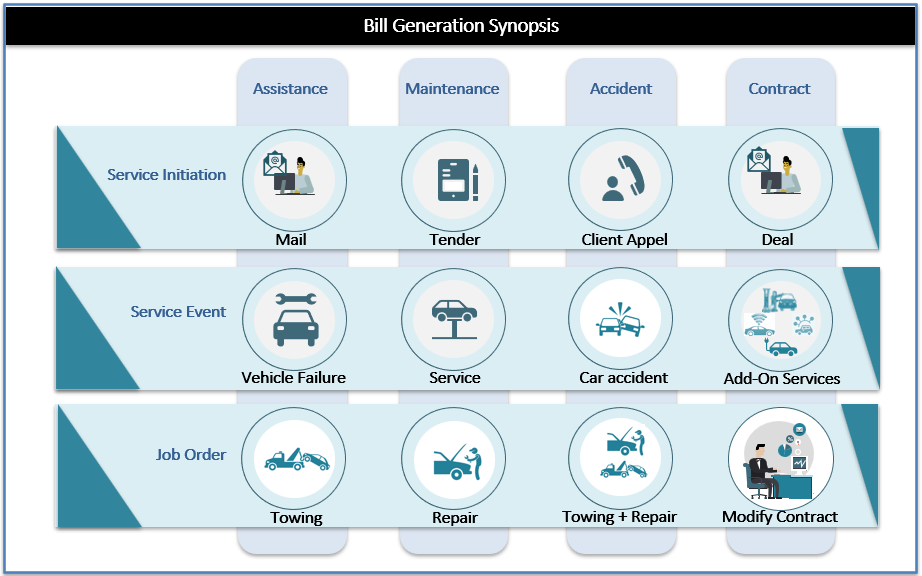
Service Initiation
The mobility solution service initiation will get triggered though various sources, for example, A mail requesting assistance, a call from customer on car accident, initialization of the contract maintenance (extension / expiry), A new tender by a corporate seeking mobility or fleet management.
Service Event
The event is a description of what took place concerning the vehicle or the end user (ex: description of mechanical breakdown, description of offence, etc.)
Job Order
The order is a description of what is ordered (ex: order of a vehicle, order of a card combustible, order of a repairing, etc.)
Revenue Management for Mobility: Solution Blueprint
Today, banks are targeting the ability to manage and operate fleets of multi-brand vehicles as a highly profitable business. A system to manage the recurring revenue from fleet is the need of the hour to become successful in the Future of Mobility.
The segment also expects more financial regulations especially on managing the risks and various reporting requirements. To comply with the standards the legacy IT systems needs adaptability.
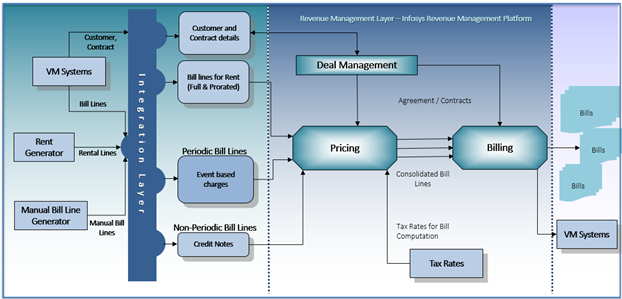
To be alive in the new age digital disruptions, Banks should equip themselves to conceive the right offerings in line with the new age market trends & business models aligned with customer expectation. Basically, banks need a revenue management solution that can monetize the transactions generated across its ecosystems.
Infosys Revenue Management Platform is a highly configurable Billing & revenue management system for banks with inbuilt business functions and pre-defined interfaces to handle the Mobility Solutions.