Executive Summary
As organizations rapidly migrate to the cloud in pursuit of agility and innovation, many face the unintended consequences of rising costs and limited visibility—creating a cloud paradox. FinOps offers a strategic, value-driven approach to managing cloud spend through cultural alignment, structured frameworks, and operational maturity. This paper outlines how a managed care organization transformed its cloud operations with a phased FinOps model—moving from reactive cost control to proactive optimization. By implementing governance, automation, and cross-functional collaboration, enterprises can turn cloud costs into a catalyst for growth and business value.
Organizations are embracing the cloud at an unprecedented pace, driven by promises of agility, scalability, and innovation. However, this transformative journey often leads to a stark reality: uncontrolled cloud spending, obscured visibility, and a widening gap between technology investments and business outcomes. This is the cloud paradox – a landscape where the very tools meant to empower, instead, become sources of financial strain and operational complexity.
From Cloud Cost to Business Catalyst: The FinOps Transformation
To navigate this paradox, organizations need a strategic compass: FinOps. Financial Operations (FinOps) transcends mere cost control; it’s a cultural shift, a strategic framework, and a set of actionable practices that align cloud spending with business value. This thought paper introduces a comprehensive approach to FinOps, guiding organizations from reactive cost management to proactive value creation.
Beyond Reactive: The Proactive Leap in Managed Care
For one managed care organization, the cloud paradox became a pressing reality. Faced with escalating cloud costs and a lack of visibility, they embarked on a FinOps maturity journey. This wasn’t just about cutting costs; it was about transforming their cloud operations into a strategic asset. By partnering with experts, they implemented a two-pronged approach: reducing cloud waste and enhancing FinOps maturity. The results were tangible: immediate cost savings, a defined target maturity state, and a multi-year roadmap for continuous improvement.
Cloud Command: Mastering Your Spend with a FinOps Framework
The FinOps Framework for managing cloud financial operations, as depicted here, is structured around core principles, operational phases, maturity stages, and key domains. At the heart of FinOps lies the need for collaborative teamwork, shared ownership of cloud usage, and centralized oversight to drive efficiency. The framework emphasizes transparency through accessible reporting and decision-making grounded in business value, leveraging the cloud’s variable cost model for optimal financial outcomes.
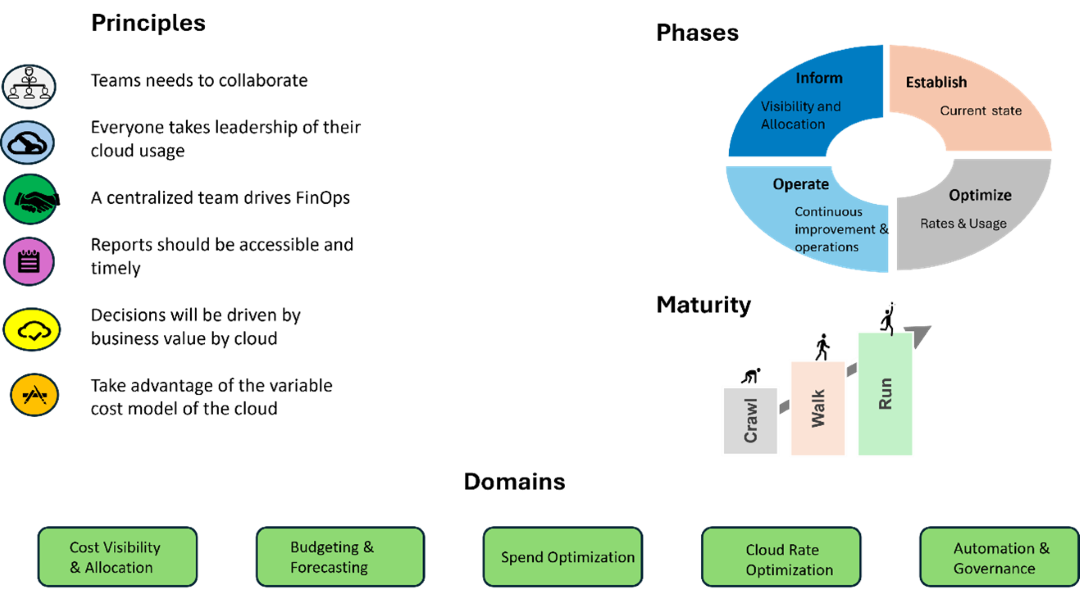
FinOps unfolds across distinct phases: establishing visibility and allocation, operating for continuous improvement, and optimizing rates and usage. These phases are supported by a maturity model that progresses from “crawl” to “run,” indicating increasing sophistication in FinOps practices. The framework is further structured around critical domains, including cost visibility and allocation, budgeting and forecasting, spend and cloud rate optimization, and automation and governance. Together, these elements form a comprehensive approach to cloud financial management, enabling organizations to effectively control costs while maximizing the benefits of their cloud investments.
FinOps: Mastering Cloud Economics, One Phase at a Time
To implement the FinOps Framework effectively, organizations should follow a structured approach:
1. Inform: Current State Assessment to Implementation Roadmap:
- This phase begins with a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s current FinOps maturity. Questionnaires, like those outlined in the document, delve into key domains: cost visibility, budgeting, spend optimization, automation, and collaboration. This assessment provides a clear picture of the “crawl” stage, highlighting areas for improvement.
- From this assessment, a tailored implementation roadmap is crafted, outlining the steps to progress through the “walk” and “run” stages.
Detailed Assessment Components:
- Cost Visibility & Allocation: Evaluating real-time cost tracking, tagging strategies, and chargeback/show back implementations.
- Budgeting & Forecasting: Analyzing budget alignment with business objectives and forecasting accuracy.
- Spend Optimization: Assessing resource rightsizing and utilization of reserved instances/savings plans.
- Automation & Governance: Reviewing anomaly detection and cost policy automation frequency.
- Collaboration & Culture: Examining cross-functional team collaboration and cost review practices.
Implementation Roadmap:
This roadmap outlines specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities for each phase of the FinOps journey. It includes establishing cloud governance, implementing tagging and show back policies, utilizing historical data for budgeting, automating cost controls, and developing comprehensive reporting dashboards.
2. Operate: FinOps Operating Model:
The “Operate” phase centers on building a robust and collaborative FinOps operating model, defining how Finance, Engineering, and Business teams work together to strategically manage cloud expenditures. This model ensures cloud spending is transparent, optimized, and directly aligned with overarching business objectives.
Key Components of an Effective FinOps Operating Model:
- FinOps Governance: Policy and Accountability: This component establishes clear policies, best practices, and lines of accountability for cloud financial management. It ensures consistent adherence to financial guidelines and promotes responsible cloud usage across the organization.
- People: Collaborative Teams and Leadership:
Building a dedicated FinOps team or Center of Excellence (COE) is crucial. This team, led by a designated FinOps lead, fosters cross-functional collaboration and ensures that all stakeholders—Finance, Engineering, and Business—are actively involved in cloud cost management. - Process: Streamlined Workflows and Controls:
This involves implementing efficient processes for cloud governance, including tagging strategies, show back/chargeback policies, budgeting and forecasting methodologies, and automated cost control mechanisms. These processes aim to create a structured and predictable financial environment. - Tools: Enabling Visibility and Optimization:
Leveraging the right tools is essential for effective FinOps. This includes utilizing reporting and visualization platforms like Power BI, cost monitoring tools like AWS Cost Explorer, budgeting and forecasting solutions like Apptio and Anodot, and workflow management systems like ServiceNow. These tools provide the necessary data and automation to drive informed decisions and optimize cloud spending.
3. Optimize: Implementation of Roadmap:
This phase focuses on executing the roadmap, transitioning from basic cost visibility to automated, strategic financial management. This involves implementing tools like Power BI for reporting, cloud-native tagging tools, and budgeting platforms like Apptio.
Maturity Progression:
- Crawl: Establishing basic cost visibility and governance.
- Walk: Implementing budgeting, forecasting, and rightsizing strategies.
- Run: Automating cost controls, enabling anomaly detection, and tracking key performance indicators.
The KPI Framework: Measuring and Driving Success
To ensure continuous improvement, organizations need a robust KPI framework. This framework, tailored to each maturity level, allows for precise measurement and tracking of FinOps capabilities. By benchmarking against industry peers and regularly reviewing KPIs, organizations can ensure their FinOps practices remain aligned with best practices.
KPI Categories:
- Cost Efficiency: Cost per workload, cost per user/transaction, and resource utilization.
- Budget Accuracy: Variance between budgeted and actual cloud spend.
- Forecast Accuracy: Accuracy of cloud spend predictions.
- Automation Effectiveness: Percentage of automated cost control and optimization processes.
- Collaboration & Communication: Frequency of cross-functional team meetings and cost reviews.
Benefits of KPI Tracking:
- Provides insights into the effectiveness of FinOps practices.
- Identifies areas for improvement and optimization.
- Enables data-driven decision-making.
- Facilitates benchmarking and performance tracking.
Conclusion: Transforming Cloud Costs into a Strategic Advantage
FinOps is not a one-time project, but a continuous journey. By adopting a structured approach, organizations can transform their cloud cost management from a reactive burden into a strategic advantage. This allows them to not only optimize cloud investments but also drive innovation, enhance agility, and ultimately, deliver greater business value. Implementing FinOps is an investment in the organization’s future, and cloud success.
References:
- FinOps Foundation Insights: FinOps Framework 2025 by FinOps Framework Overview
- FinOps Framework Article published by Microsoft published by Flanakin and Bandersmsft : FinOps Framework overview – Cloud Computing | Microsoft Learn