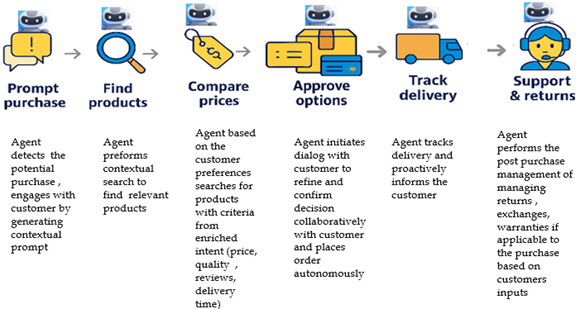
What is Agentic Commerce
E-commerce has evolved from brick-and-mortar stores to immersive websites, to intuitive mobile apps, and now it’s stepping into a new era of Agentic Commerce. Agentic commerce is an emerging paradigm in which autonomous, context-aware AI agents orchestrate end-to-end shopping workflows on behalf of the customers. These agents leverage predictive analytics, personalization algorithms, and automated decision-making to anticipate user needs, optimize interactions, and execute transactions seamlessly, delivering frictionless and proactive commerce experiences. These autonomous AI agents are next-generation software solutions powered by large language models (LLMs). They don’t just chat, they think, decide, and act autonomously, transforming human interaction into intelligent actions. Unlike traditional e-commerce, agentic commerce is intent-driven, context-aware, and action-oriented, enabling frictionless experiences with minimal human intervention.
Agentic commerce is evolving through three primary interaction models: Agent-to-Site, Agent-to-Agent, and Brokered Agent-to-Site.
Agent-to-Site: AI agents interact directly with merchant platforms. For example: The grocery-shopping agent visits multiple supermarket websites, compares prices for customers preference products, and completes the checkout on approval of the cart by the customer.
Agent-to-Agent: AI agents transact autonomously with other agents. For instance, a healthcare agent collaborates with a pharmacy’s AI agent to reorder prescriptions and apply insurance benefits without user intervention
Brokered Agent-to-Site: Intermediary systems facilitate multi-agent and multi-platform interactions. For instance, a healthcare agent collaborates with a pharmacy’s AI agent to reorder prescriptions and apply insurance benefits without user intervention
Core Components of Agentic Commerce
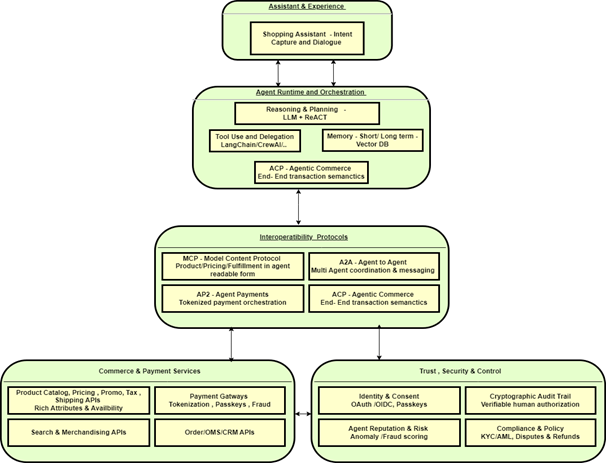
The components of Agentic commerce are
- Intelligent agents – brain of the agentic commerce, which understand the intent, powered by LLM. The different types of agents are Buyer, Seller, Service and Fulfillment agents Agent Orchestration layer – coordination and governance layer managing multiple agents’ interaction powered by workflow engines, model routers and context sharing protocols (MCP). Routing between agents, conversation contexts, decision logic, and rules enforcement is managed.
- Commerce data layer – structured information environment which feeds agent decisions powered by vector DBs, knowledge graphs, RAG pipeline.
- Commerce API Infra – connectivity layer linking agents to real world commerce systems powered by platforms. It includes APIs for Products, pricing, …fulfillment
- Payment and Identity Layer – Trust and transaction foundation which helps agents buy safely. It includes Delegated payment authorization which users give controlled spending rights to agents. Digital identity and verifiable credentials prove agent legitimacy. Tokenization and auditability ensure traceable and secure transactions
- Interoperability and communication protocols – glue that allows different agents and systems to communicate to each other
o ACP – open standard for cross platform transactions
o MCP – share data, tools or reasoning context across models
o A2A – standard way for buyer and seller agents to negotiate
- Experience and Control layer – includes Conversational interfaces, explainability and override options
- Governance, Compliance and Safety – layer which ensures ethical, secure and regulatory compliance by audit logs, policy enforcement, regulatory compliance, fraud prevention
Core Technologies Enabling Agentic Commerce
The core technologies enabling shift towards agentic Commerce are
- LLMS /Foundation Models
- Protocols and Interoperability standards
- Payment, Tokenization and Trust Infrastructure
The Agentic Commerce paradigm is underpinned by a set of foundational protocols, including the Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP), Anthropic’ s Model Context Protocol (MCP), the Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol, and the Agent Payments Protocol (AP2). Each protocol addresses distinct functional domains within the ecosystem and can operate autonomously, while optional integration offers extended capabilities to advance the vision of intelligent, autonomous agents. In context to, ACP and AP2, ACP handles merchant-side integration and quick enablement of agentic commerce on existing payment rails. AP2 provides the trust and compliance layer, ensuring that transactions initiated by agents are authorized, authenticated, and auditable. In simpler words, ACP manages the checkout experience and payment orchestration, while AP2 enforces mandates and verifiable credentials, adding cryptographic proof of user consent and agent authority.
OpenAI’s Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP), is an open standard built with Stripe that empowers AI agents like ChatGPT to securely complete purchases in real time, turning conversations into checkouts.
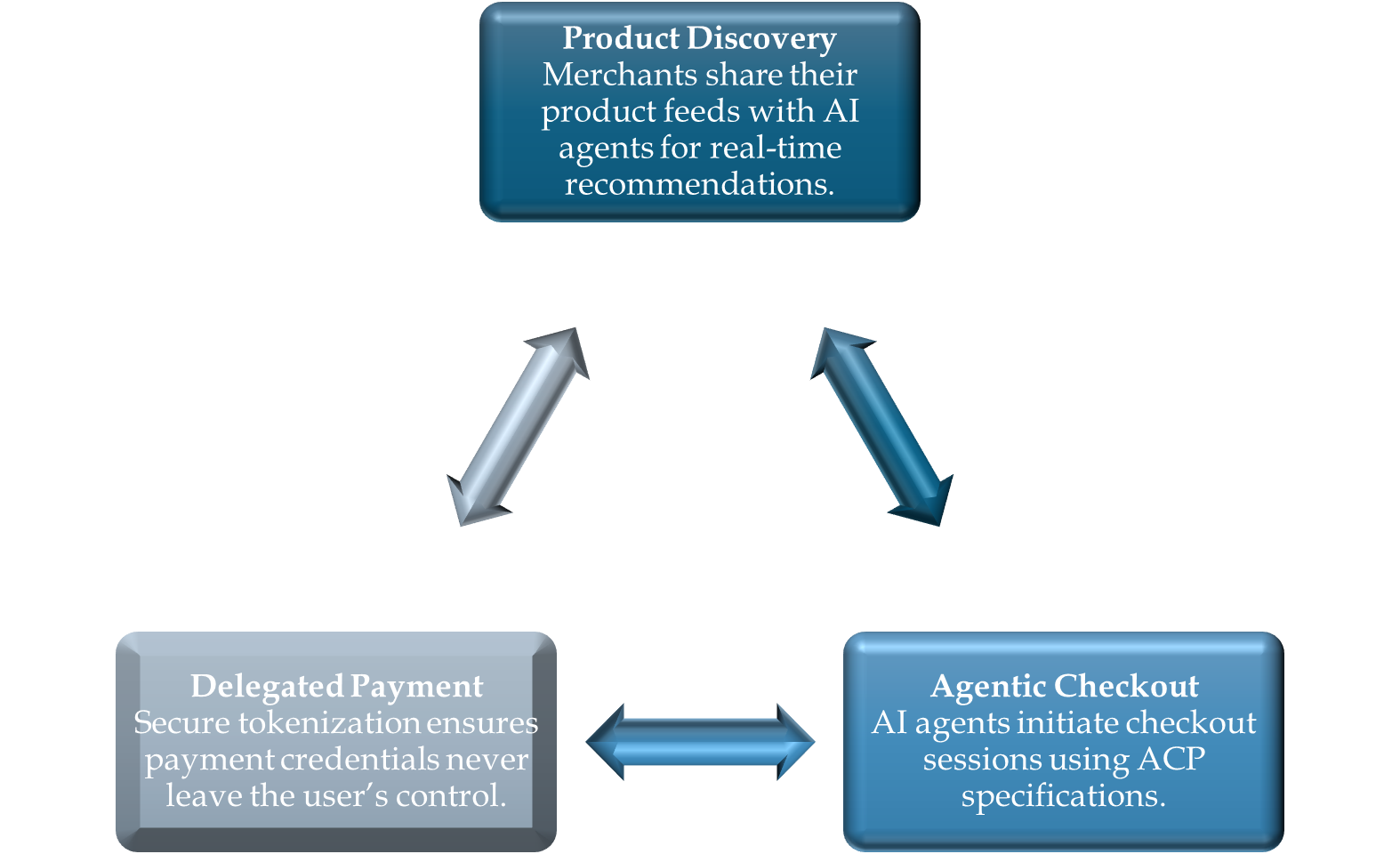
ACP is built on two sub-protocols:
- Agentic Checkout Protocol: Handles product selection, cart creation, and order workflows.
- Delegated Payment Protocol: Manages secure payment tokenization for AI-driven transactions.
- Agent Payments Protocol (AP2): Developed by Google, AP2 is payment-agnostic framework for secure transactions within the agentic environment. It aims to provide a common language for agent’s interaction and handle payments.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Introduced by Anthropic, MCP works in conjunction with ACP. Its primary role is to let agents securely query tools, APIs, and enterprise data (like search indices, catalogs, and databases) to gather the necessary context before a transaction is executed via ACP.
- Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol: This is a broader, open-source framework that creates a common language for agents to interact and collaborate on complex tasks, not just commerce. It focuses on general agent interoperability.
Proprietary/Platform-Specific Integrations: Before the rise of open standards like ACP, agentic commerce was often handled through bespoke, proprietary integrations built for specific platforms or merchants. - Proprietary/Platform-Specific Integrations: Before the rise of open standards like ACP, agentic commerce was often handled through bespoke, proprietary integrations built for specific platforms or merchants.
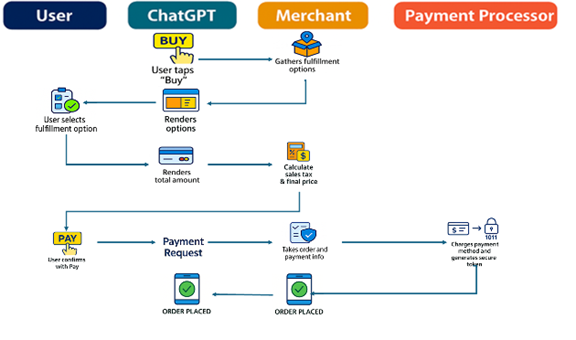
How Agentic Commerce Works
Early Adopters of Agentic Commerce
Making a significant shift toward AI-first commerce ecosystem, Etsy is the first retailer who ventured into agentic commerce on ChatGPT. ChatGPT users can buy directly from Etsy sellers within the US. Major players like PayPal and Worldpay have announced ACP integrations, enabling millions of merchants to sell via ChatGPT.
- Walmart has partnered with Open AI to create agentic commerce AI first shopping experience.
- Food and drug retailer Albertsons Cos. has deployed Google Cloud’s new Conversational Commerce agent, an AI shopping assistant
- Shopify is partnering with OpenAI to enable agentic commerce. Below pilot brands from Shopify’s premium merchant network who will be part of the initial roll out of ACP-powered Instant Checkout in ChatGPT are:
Glossier
SKIMS
Spanx
Vuori - Salesforce has announced support for the ACP in collaboration with Stripe to build Instant Checkout integrations for merchants using their Agentforce Commerce platform.
- Commercetools has joined Stripe and OpenAI as a launch partner of the ACP, enabling their global enterprise clients (such as Sephora and BMW) to participate in agent-driven commerce.
- Stripe has co-developed the ACP with OpenAI and is the primary payment processor for the initial Instant Checkout implementation in ChatGPT.
- WorldPay and PayPal have recently announced they will also support payments processing for merchants leveraging OpenAI Instant Checkout via ACP
- MasterCard has launched Agent Pay Acceptance Framework to support agentic commerce
- Salsify has introduced new artificial intelligence (AI) tools aimed at automating product experience management (PXM) workflows and linking brands more directly to AI-powered shopping platforms.
- Williams-Sonoma is leveraging Salesforce Agentforce 360 is using agentic AI as interior design agents which helps in providing personalized consumer experience and products and for autonomous customer support
Agentic Commerce Use Cases across Industries
| Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Shopping | AI agents use user preferences to make autonomous purchasing decisions. For example, an agent might order groceries based on past purchases and dietary requirements, reducing manual effort for the consumer. | Tailored recommendations and improving customer satisfaction. |
| Product Discovery & Recommendation | Agentic systems act as personal shopping assistants that understand user preferences, budget, and context. They can handle requests sent via text, find and compare products, and complete purchases autonomously. These agents also help users discover products through images and recover abandoned carts by offering reminders or incentives. | Saves time for customers by eliminating manual search, improving personalization and conversion rates for retailers, Reduces decision fatigue for consumers |
| Dynamic Pricing & Bundling | Agents negotiate prices and create bundles in real-time. Example: An agent finds the best deal for electronics across multiple platforms. | Maximizes cost savings and enhances purchasing efficiency. |
| Marketing | AI agents study customer behavior and automatically create highly personalized marketing campaigns across channels like email, social media, and apps. They continuously learn and adjust messaging to improve engagement and effectiveness. | Increases customer engagement and loyalty, Improves ROI on marketing spend, Reduces manual effort for marketing teams. |
| Autonomous Inventory Management | AI predicts demand and reorders stock automatically. Example: Retail agent replenishes shelves before stock-outs occur. | Reduce operational delays and prevent lost sales. |
| Smart Warehousing | AI agents can manage robots for tasks like picking and packing in automated fulfillment centers. This coordination streamlines operations, speeds up order processing, and reduces manual labor. | Improves speed and accuracy in processing. |
| Automated Procurement & Payments | AI agents can manage B2B purchases and payment workflows, streamlining procurement and financial processes. For example, a corporate agent might autonomously order office supplies and handle invoice processing, reduce manual effort and improve efficiency. | Cuts administrative overhead and ensures compliance. |
| Predictive Maintenance | AI agents can schedule repairs by analyzing sensor data and predicting issues before they occur. For example, a manufacturing agent might order spare parts in advance to prevent machine failure, reducing downtime and improving efficiency. | Minimizes downtime and reduces maintenance costs. |
| Travel Booking | AI agents can plan and manage travel by booking flights, hotels, and organizing itineraries. For example, an agent can handle an entire business trip end-to-end, saving time and reducing manual effort for travelers. | Saves time and optimizes travel costs. |
| Healthcare Supply Ordering | AI agents can manage healthcare logistics by reordering medical supplies and handling insurance claims. For example, a hospital agent ensures timely delivery of critical equipment, reducing delays and improving patient care. | Improves patient care and operational efficiency. |
What are the Strategic Shifts Required by Business to Embrace Agentic Commerce
To embrace Agentic Commerce, businesses need to make strategic shifts across technology, operations, and customer engagement. The key areas:
Re-architect Digital Foundations:
- Machine-readable catalogs & APIs: Product, pricing, and inventory data must be structured and accessible for AI agents. Slow or incomplete APIs will make brands invisible to agent-driven shopping.
- Real-time infrastructure: Systems must handle machine-speed queries and transactions without latency. This requires cloud-native, event-driven architecture.
Build an Agent-Ready Ecosystem:
- Interoperability protocols: Adopt standards like MCP, A2A, AP2, ACP for agent-to-agent communication and secure payments.
- Agent-facing interfaces: Create “front doors” for AI agents viz. APIs, registries, and trust signals, so they can discover and transact with the host system.
Establish a Trust & Governance Stack
- Agent verification & fraud controls: Differentiate legitimate agents from malicious ones.
- Human-in-the-loop for high-value transactions: Maintain oversight for compliance and trust.
- Transparent policies: Liability, refunds, and explainability frameworks to reassure customers and regulators.
Reinventing Customer Engagement
- Brand visibility in AI ecosystems: Optimize for platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity where agents operate. Launch branded AI agents to maintain direct engagement and loyalty.
- Marketing: Product marketing must shift to agentic discoverability from SEO to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) Agents may bypass ads and traditional funnels, API monetization, subscription models, and agent partnerships will have to be relooked
Data Strategy Overhaul
- Move from static to dynamic data: Real-time streams for inventory, pricing, and personalization.
- Break down silos: Unified, orchestrated data accessible via secure protocols like MCP
Challenges, Risks and Governance Needs
Key challenges of Agentic Commerce:
Interoperability & Standards
- Each commerce platform is building their own agentic framework, leading to lack of common protocols across agent-to-agent communication across platforms. While ACP, MCP and A2P protocols aim to address the interoperability issues in Agentic Commerce. But adoption of them is in nascent stages and are not universally adopted. Without standardized protocols for identity, verification and transaction logging, it is hard to establish trust between agents. Protocols are also needed for safe data sharing, with lack of wider adoption of standards making compliance and security harder. Visa’s Trusted Agent Protocol and Mastercard’s Agent Pay Acceptance Framework aim to verify agent identity and intent.
Data & Metadata Challenges
- AI agents depend on accurate, structured product data to make decisions. When metadata is incomplete or incorrect, agents can misinterpret product details, leading to wrong purchases, higher return rates, and dissatisfied customers. Structured metadata will become a competitive differentiator for brands adopting agentic commerce.
Complex Decision-Making
- The agents designed in the Agentic Commerce should balance cost, quality, ethics, and user preferences autonomously. Meticulous design of agents will be warranted with weighed scoring models or Pareto optimization for each dimension with configurable weight which should be dynamic based on the context. For example: Score=wc⋅Cost+wq⋅Quality+we⋅Ethics+wu⋅UserPref. Agents should use constraint solvers to prune options before negotiation.
User Trust
- With AI agents making purchasing decisions, accountability becomes unclear. Existing return and refund policies will need to be formalized for agent-driven transactions, to address the significant gaps in liability. For example: If an agent makes a wrong purchase or violates existing subscription contract, the policies around agent driven transactions should be strongly defined to gain consumer trust. Transparent agent behavior, opt-in controls, and educational campaigns can help to bridge the trust gap.
Key risks of Agentic Commerce:
Security & Fraud
- Agents could be hacked or manipulated to make unauthorized purchases.
Bias & Fairness
- Algorithms may favor certain vendors, leading to anti-competitive practices.
Data Privacy
- Agents require deep access to personal data, increasing exposure risk.
Financial Exposure
- Autonomous agents might overspend or make poor decisions without oversight.
Primary Governance Needs of Agentic Commerce:
Regulatory Framework
- Clear rules for agent behavior, liability, and compliance with consumer protection laws.
Auditability
- Transparent logs of agent decisions for accountability.
Ethical Guidelines
- Standards for fairness, sustainability, and non-discrimination in commerce.
Identity & Authentication
- Strong mechanisms to verify agent identity and prevent impersonation.
Human Oversight
- Ability for users or regulators to override or halt agent actions instantly.
Market Forecasts
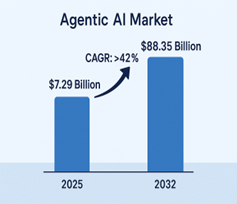
McKinsey projects that the global agentic commerce market could reach between $3 trillion and $5 trillion by 2030, with the U.S. retail sector alone contributing up to $1 trillion. This surge is fueled by AI’s capability to enable intent-driven shopping, minimize friction, and support autonomous decision-making across multiple platforms. In the near term, Warc Media estimates the total addressable market at $136 billion in 2025, fueled by rapid adoption in retail media and e-commerce. By 2030, this figure could surge to $1.7 trillion, as brands and marketplaces integrate agent-ready platforms and protocols like Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP) and Agent Payments Protocol (AP2). Parallel to commerce, the Agentic AI market, the underlying technology is expected to grow from $7.29 billion in 2025 to $88.35 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of over 42%, reflecting enterprise adoption for automation and decision-making. By 2030, McKinsey estimates that agentic commerce could generate up to $1 trillion in revenue within the U.S. B2C retail sector alone, while global figures may range between $3 trillion and $5 trillion.

References
https://developers.openai.com/commerce/
https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/agentic-ai-market-114233
https://www.darwinium.com/resources/the-evolution-blog/trust-and-risk-agentic-commmerce
https://www.techrepublic.com/article/agentic-commerce/
McKinsey forecasts up to $5 trillion in agentic commerce sales by 2030
Agentic Commerce is a Huge Opportunity for Retailers; it’s Also a Liability Storm
Agentic Commerce is a Huge Opportunity for Retailers; it’s Also a Liability Storm