In our previous article, we explored the remarkable journey of QR codes from Toyota’s factory floors to powering a $16.8 billion global payment market. We examined the technical capabilities that make this growth possible and the impressive adoption statistics across different regions. Now, let’s dive into what’s really driving this adoption: the tangible benefits that make QR code payments irresistible to both consumers and merchants.
Convenience Redefined:
Pocket-Sized Payment Power
The most compelling advantage for consumers is sheer convenience. QR code payments eliminate the need to carry physical cash or multiple cards, a smartphone is all that’s required. This simplification resonates particularly strongly in our increasingly digital world, where consumers expect seamless experiences across all interactions.
Transaction processing happens in seconds rather than minutes. There’s no fumbling with change, no waiting for card readers, no signature requirements for small purchases. The 24/7 availability means payments can be processed any time without dependency on traditional banking hours, making late-night purchases or early morning transactions effortless.
Enhanced User Experience
QR code payments deliver a superior user experience through simplified processes that require only smartphone camera functionality. Digital receipt storage eliminates paper waste while providing instant access to transaction history. The reduced data entry requirements minimize user errors, no more typing long card numbers or accidentally selecting the wrong payment method.
Integration with loyalty programs provides immediate rewards, allowing consumers to earn points, receive discounts, and access special offers seamlessly within the same transaction flow. This integration transforms routine purchases into engaging experiences that build customer loyalty.
Financial Inclusion
Perhaps most importantly, QR code payments enable participation in the digital economy for individuals without access to traditional banking services. In developing markets, this technology supports crucial financial inclusion initiatives, allowing previously underserved populations to engage in digital commerce without requiring extensive banking relationships or credit histories.
This democratization of digital payments has profound social and economic implications, enabling small vendors in remote areas to accept digital payments and participate in the broader economy.
The Merchant Advantage:
Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
Traditional payment systems often burden merchants with substantial fees. Credit and debit card transaction processing typically involves multiple fee layers, expensive hardware requirements, and ongoing maintenance costs. QR payments significantly reduce these expenses through lower transaction fees, reduced infrastructure requirements, and elimination of expensive POS hardware for basic transactions.
Consider the real-world comparison: A traditional EFTPOS solution provider impose transaction fees of 1.4% for businesses processing less than $20,000 monthly, plus monthly terminal rental fees of $29. One of the Big 4 Australian bank’s smart terminal charges 1.1% transaction fees with additional rental costs, while another big bank charges 1.2% to 1.4% transaction fees plus $24 to $28 monthly terminal fees.
In contrast, QR code payment implementations eliminate hardware requirements for basic operations, removing capital expenditure burdens associated with dedicated terminal infrastructure. This typically results in reduced transaction fees while lowering barriers to entry for small merchants who find traditional EFTPOS solutions prohibitively expensive.
Operational Efficiency Improvements
QR payments streamline operations through instant transaction processing that reduces queue times and improves customer throughput. Automated payment confirmation eliminates manual verification steps, while integration with inventory and accounting systems provides real-time business insights.
Reduced cash handling requirements minimise security risks associated with physical money management, from theft concerns to time-consuming counting and banking procedures. Staff can focus on customer service rather than payment processing logistics.
Business Intelligence and Customer Insights
QR payment systems generate valuable data about customer purchasing behaviour, transaction patterns, and preferences. This information enables targeted marketing campaigns, personalised offers, and improved inventory management based on actual buying trends rather than guesswork.
Integration with customer relationship management (CRM) systems allows businesses to build comprehensive customer profiles, track lifetime value, and develop retention strategies based on real transaction data. Small businesses gain access to sophisticated analytics previously available only to large corporations with extensive IT resources.
Environmental and Social Impact
QR code payments support sustainability initiatives through reduced paper receipt generation, elimination of plastic card production, and lower carbon footprint from reduced physical payment infrastructure. Many environmentally conscious consumers actively choose businesses that offer sustainable payment options.
Security:
Multi-Layer Protection
QR code transactions incorporate comprehensive security measures that often exceed traditional payment methods. End-to-end encryption protects transaction data during transmission, while dynamic QR codes continuously change information to prevent replay attacks. Multi-factor authentication requirements enhance security through biometric verification, PINs, or passwords.
Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with secure tokens, ensuring that actual account information never travels through merchant systems. This approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches affecting customer financial information.
Advanced Fraud Prevention
Modern QR payment systems employ sophisticated fraud detection techniques. Time-sensitive codes expire after predetermined periods, preventing unauthorized reuse of payment information. Transaction-specific codes ensure each payment contains unique verification data that cannot be replicated.
Real-time fraud monitoring systems detect suspicious activity patterns and can block potentially fraudulent transactions before they complete. Biometric authentication adds additional security layers that are extremely difficult to compromise.
Payment Process Models:
Merchant-Presented QR Codes
The most common implementation involves merchants displaying QR codes for customer scanning. The process flows seamlessly: customers encounter the QR code at point of sale, open their payment application, scan the merchant’s code, review transaction details, authorise payment using biometric authentication or PIN, and receive confirmation along with digital receipts.
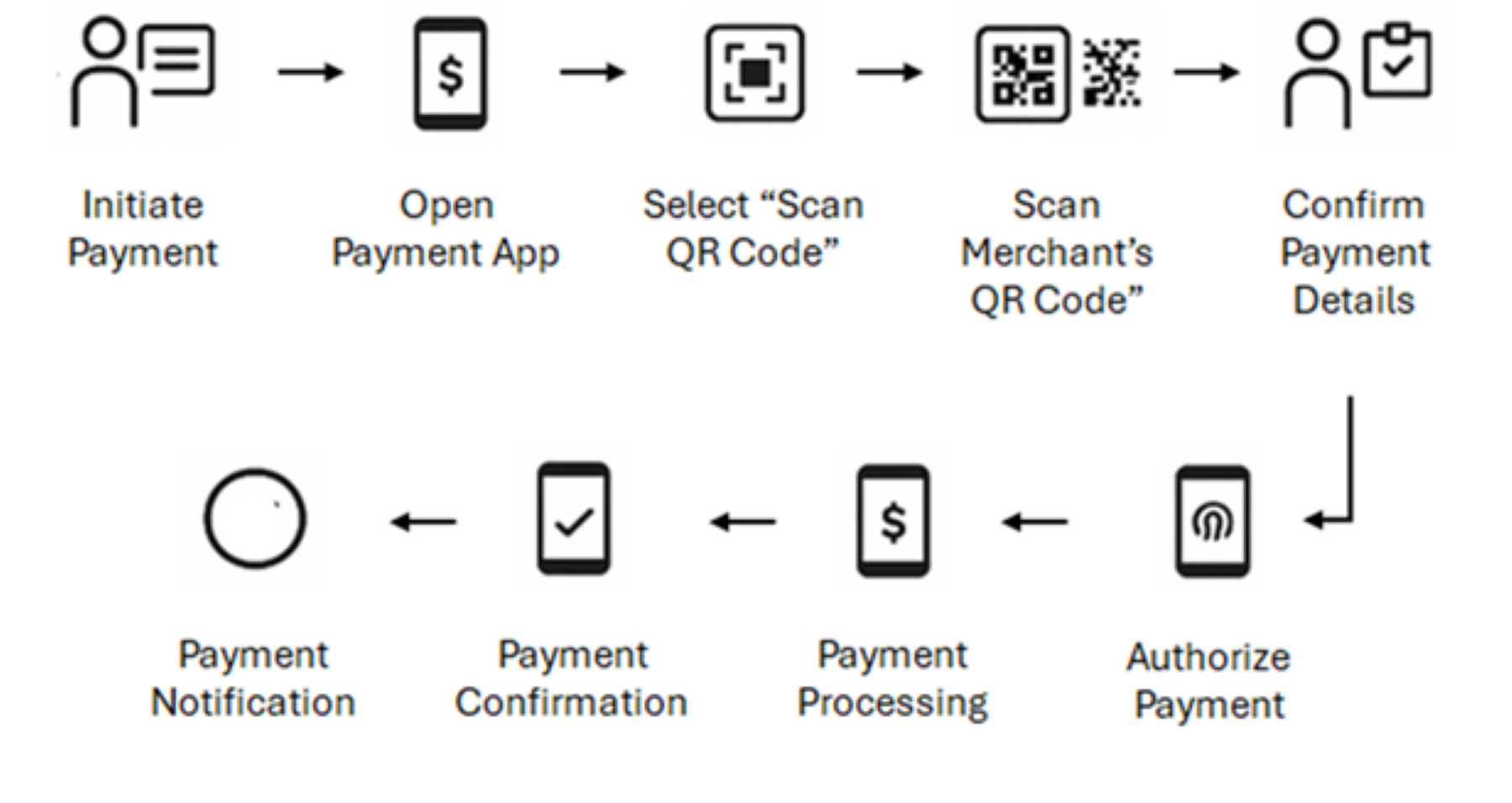
Static codes work well for basic merchant identification, while dynamic codes include transaction-specific information like amounts and timestamps for enhanced security and real-time processing.
Customer-Presented QR Codes (Reverse QR)
This model enables customers to display QR codes for merchant scanning, providing enhanced customer control over the payment process. Customers generate unique, time-sensitive codes in their payment apps, merchants scan these codes using POS terminals or mobile devices, enter transaction amounts, and process payments through established networks.
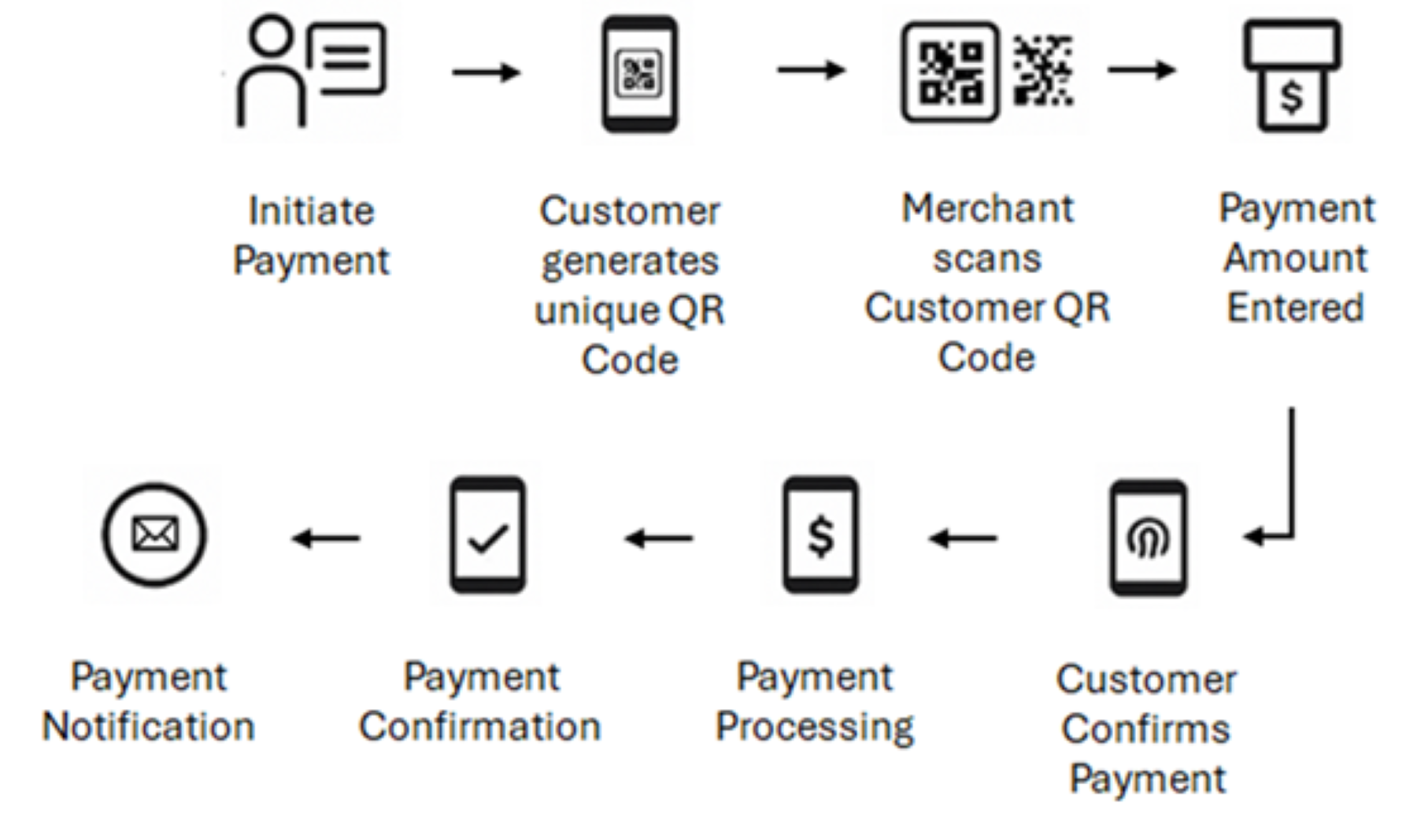
This approach reduces QR code tampering risks since customers generate their own secure codes rather than relying on potentially compromised merchant-displayed codes.
Competitive Positioning in the Digital Ecosystem
QR codes offer unique advantages over alternative payment technologies. Universal smartphone compatibility eliminates NFC hardware requirements that restrict payment accessibility. All smartphones can read QR codes, enabling wider market reach compared to NFC solutions requiring specific hardware capabilities.
Implementation costs remain lower than contactless card systems, as merchants can deploy QR solutions without investing in specialised terminal infrastructure. Enhanced transaction data capture capabilities enable comprehensive customer interaction tracking that traditional contactless methods cannot provide.
Addressing the Challenges Ahead
While the benefits are compelling, successful QR code payment implementation requires addressing several challenges. Consumer concerns about financial data security need addressing through robust education programs and transparent security practices. Merchant implementation barriers include initial setup costs, staff training requirements, and integration with existing systems.
Infrastructure requirements involve reliable internet connectivity, regulatory compliance across jurisdictions, and standardisation across platforms for seamless interoperability.
Future Outlook
QR codes represent one of technology’s most unexpected success stories. The projected growth reflects fundamental advantages in convenience, cost-effectiveness, security, and accessibility.
Organisations that strategically embrace QR code payments will be best positioned to thrive in this digital payment revolution. The key lies not just in implementing the technology, but in understanding how it fits into broader digital transformation strategies that serve customers, reduce costs, and create sustainable competitive advantages.
The future belongs to organisations that recognise QR codes not as a simple payment method, but as a platform for enhanced customer relationships, operational efficiency, and business growth. The opportunity awaits those ready to act strategically and collaboratively in shaping the next phase of digital commerce.